150 mg, 300 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
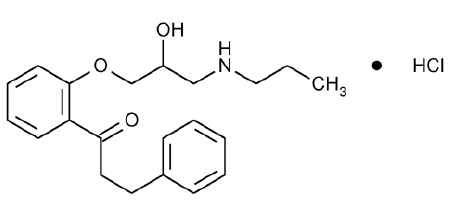
PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS (Propafenone Hydrochloride) is a class IC antiarrhythmic with some negative inotropic and beta-adrenoceptor blocking activity. Chemically, Propafenone hydrochloride is 1-Propanone,1-[2-[2-hydroxy-3-propylamino)propoxy]phenyl]-3-phenyl-,hydrochloride.The molecular formula is C21H27NO3·HCl and molecular weight is 377.90.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are white coloured, circular, biconvex film coated tablets.
COMPOSITION :
Each film coated tablet contains :
Propafenone Hydrochloride USP 150 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide USP
Each film coated tablet contains :
Propafenone Hydrochloride USP 300 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide USP
ACTIONS :
Propafenone is a class IC anti-arrhythmic agent. It has a stabilising action on myocardial membranes, reduces the fast inward current carried by sodium ions with a reduction in depolarisation rate and prolongs the impulse conduction time in the atrium, AV node and primarily, in the HIS-Purkinje system. Impulse conduction through accessory pathways, as in WPW syndrome, is either inhibited, by prolongation of the refractory period or blockade of the conduction pathway, both in anterograde but mostly retrograde direction. At the same time, spontaneous excitability is reduced by an increase of the myocardial stimulus threshold while electrical excitability of the myocardium is decreased by an increase of the ventricular fibrillation threshold. Anti-arrhythmic effects : Slowing of upstroke velocity of the action potential, decrease of excitability, homogenisation of conduction rates, suppression of ectopic automaticity, lowered myocardial disposition to fibrillation.Propafenone has moderate beta-sympatholytic activity without clinical relevance. However, the possibility exists that high daily doses (900 - 1200 mg) may trigger a sympatholytic (anti-adrenergic) effect.
In the ECG, propafenone causes a slight prolongation of P, PR and QRS intervals while the QTC interval remains unaffected as a rule. In digitalised patients with an ejection fraction of 35-50 %, contractility of the left ventricle is slightly decreased. In patients with acute transmural infarction and heart failure, the intravenous administration of propafenone may markedly reduce the left ventricular ejection fraction but to an essentially lesser extent in patients in the acute stages of infarction without heart failure. In both cases, pulmonary arterial pressure is minimally raised. Peripheral arterial pressure does not show any significant changes. This demonstrates that propafenone does not exert an unfavourable effect on left ventricular function which would be of clinical relevance. A clinically-relevant reduction of left ventricular function is to be expected only in patients with pre-existing poor ventricular function. Untreated heart failure might then deteriorate possibly resulting in decompensation.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Propafenone is readily and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is metabolized in the liver, largely by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP2D6, but also to a small extent by CYP1A2 and CYP3A4; the extent of metabolism is genetically determined. In subjects with the extensive metaboliser phenotype there is extensive first-pass metabolism to two active metabolites, 5-hydroxypropafenone and N-depropylpropafenone, and to other minor inactive metabolites.In the small proportion of subjects with the slow metaboliser phenotype (lacking CYP2D6) little or no 5-hydroxypropafenone is formed. The bioavailability of propafenone is dependent upon metaboliser phenotype but more importantly on dosage as the first-pass metabolism is saturable. In practice doses are high enough to compensate for differences in phenotype. Propafenone and its metabolites also undergo glucuronidation. Propafenone is more than 95% protein bound. Propafenone is excreted in the urine and faeces mainly in the form of conjugated metabolites. The elimination half-life is reported to be 2 to 10 hours in extensive metabolisers and 10 to 32 hours in slow metabolisers. Propafenone crosses the placenta and is distributed into breast milk.
INDICATIONS :
PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of ventricular arrhythmias. PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is also indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachyarrhythmias which include paroxysmal atrial flutter/fibrillation and paroxysmal re-entrant tachycardias involving the AV node or accessory bypass tracts, when standard therapy has failed or is contra-indicated.
Administration :
PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is for oral administration.
Dosage :
It is recommended that Propafenone therapy should be initiated under hospital conditions, by a physician experienced in the treatment of arrhythmias. The individual maintenance dose should be determined under cardiological surveillance including ECG monitoring and blood pressure control. If the QRS interval is prolonged by more than 20 %, the dose should be reduced or discontinued until the ECG returns to normal limits.
Adults :
Initially, 150 mg three times daily increasing at a minimum of three-day intervals to 300 mg twice daily and if necessary, to a maximum of 300 mg three times daily. The tablets should be swallowed whole and taken with a drink after food. A reduction in the total daily dose is recommended for patients below 70 kg bodyweight.
Elderly :
Higher plasma concentrations of propafenone have been noted during treatment. Elderly patients may therefore respond to a lower dose.
Children :
A suitable dosage form of PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS for children is not available.
Dosage in impaired liver function :
Propafenone is extensively metabolised via a saturable hepatic oxidase pathway. In view of the increased bioavailability and elimination half-life of propafenone, a reduction in the recommended dose may be necessary.
Dosage in impaired renal function :
Although the elimination of propafenone and its major metabolite is not affected by renal impairment, Propafenone should be administered cautiously.
CONTRAINDICATION :
Known hypersensitivity to propafenone or to any of the other ingredients. PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is contra-indicated in patients with uncontrolled congestive heart failure, cardiogenic shock (unless arrhythmia-induced), severe bradycardia, uncontrolled electrolyte disturbances, severe obstructive pulmonary disease or marked hypotension. PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS may worsen myasthenia gravis. Unless patients are adequately paced PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should not be used in the presence of sinus node dysfunction, atrial conduction defects, second degree or greater AV block, bundle branch block or distal block. Minor prolongation of the PR interval and intra-ventricular conduction defects (QRS duration of less than 20%) are to be expected during treatment with PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS and do not warrant dose reduction or drug withdrawal. Due to the potential for increased plasma concentrations, co-administration of ritonavir and Propafenone Hydrochloride is contraindicated. PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
The weak negative inotropic effect of PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS may assume importance in patients predisposed to cardiac failure. In common with other anti-arrhythmic drugs, PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS has been shown to alter sensitivity and pacing threshold. In patients with pacemakers, appropriate adjustments may be required. There is potential for conversion of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation to atrial flutter with accompanying 2:1 or 1:1 conduction block. Because of the beta-blocking effect, care should be exercised in the treatment of patients with obstructive airways disease or asthma. As with some other class IC anti-arrhythmic agents, patients with structural heart disease may be predisposed to serious adverse effects. It is essential that each patient given PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS be evaluated electrocardiographically and clinically prior to and during therapy to determine whether the response to PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS supports continued treatment. PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : Category C.
Adequate and well-controlled studies in humans have not been done.Studies in rats and rabbits at doses of up to 40 and 10 times the maximum recommended human dose, respectively, have not shown that PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS causes teratogenicity in the fetus; however, a perinatal and postnatal study in rats at doses of 6 times the maximum recommended human dose or greater found a dose-related increase in maternal and neonatal mortality, decreased maternal and pup body weight gain, and reduced neonatal physiological development.It has not shown that Propafenone causes teratogenicity in the fetus; however, a perinatal and postnatal study. at doses of 6 times the maximum recommended human dose or greater found a dose-related increase in maternal and neonatal mortality, decreased maternal and pup body weight gain, and reduced neonatal physiological development.
Nursing mother :
Propafenone and 5-hydroxypropafenoe, a metabolite of propafenone, are distributed into breast milk at concentrations lower than those found in maternal plasma. Breast-feeding is not recommended during PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS use because of the potential for adverse effects in the nursing infant.
Paediatric use :
Safety and efficacy have not been established. However, limited use of PROPAFENONE HYDROCLORIDE TABLETS in neonates, infants, and children seems to indicate that the incidence of side effects in paediatric patients is similar to that reported in adults. Proarrhythmic effects have been reported in the paediatric population , as in the adult population, including an incident of sudden death which may or may not have been related to PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS Therefore, propafenone should be used with caution in paediatric patients.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPABILITIES :
Propafenone is extensively metabolised by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, mainly by the isoenzyme CYP2D6, although CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 are also involved. Interactions may therefore occur with other drugs that are metabolised by these enzymes. Plasma-propafenone concentrations may be reduced by enzyme inducers such as rifampicin; enzyme inhibitors, such as cimetidine, fluoxetine, quinidine, and HIV-protease inhibitors, may increase plasma-propafenone concentrations. Propafenone itself may alter the plasma concentrations of other drugs, including beta blockers, ciclosporin, desipramine, digoxin, theophylline, venlafaxine, and warfarin. The absorption of propafenone may be reduced by orlistat. There may be an increased risk of arrhythmias if propafenone is given with other antiarrhythmics or arrhythmogenic drugs.
Antiarrhythmics :
Quinidine inhibits the hepatic metabolism of propafenone and has been reported to increase plasma propafenoneconcentrations in extensive metabolisers; the plasma concentration of the active 5-hydroxy metabolite was reduced and that of the N-depropyl metabolite increased but there was no change in the clinical response. Another study, 2 however, found that quinidine increased the beta-blocking effect of propafenone in extensive metabolisers, and a study in patients with refractory atrial fibrillation found that addition of quinidine to propafenone was as effective and possibly better tolerated than increasing the propafenone dose.
Antibacterials :
Rifampicin has lowered steady-state plasma concentrations of propafenone with the Rifampicin has reappearance of arrhythmia.
Histamine H2-antagonists :
Cimetidine has been reported to raise plasma-propafenone concentrations. The mean steady-state concentration increased by 22 % but the wide interindividual variability meant this change was not significant.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The following adverse events have been reported with this or other formulations of propafenone hydrochloride. A cause and effect relationship may not have been established.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders :
Leukocytopenia and/ or granulocytopenia or thrombocytopenia; agranulocytosis.
Immune system disorders :
Allergic reactions, hypersensitivity reactions (manifested by cholestasis, blood dyscrasias).
Metabolism and nutritional disorders :
Anorexia
Psychiatric disorders :
Anxiety, confusion
Nervous system disorders :
Dizziness, headache, syncope, ataxia, restlessness, nightmares, sleep disorders, extrapyramidal symptoms, vertigo, paresthesia. Rare cases of seizures have been reported.
Eye disorders :
Blurred vision
Cardiac disorders :
A marked reduction in heart rate (bradycardia) or conduction disorders (i.e. sinoatrial, atrioventricular or intraventricular block) may occur. Proarrhythmic effects which manifest as an increase in heart rate (tachycardia), or ventricular fibrillation may also occur
Vascular disorders :
Hypotension, including postural hypotension and orthostatic hypotension
Gastrointestinal disorders :
Nausea, vomiting, constipation, dry mouth, bitter taste, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, bloating and retching
Hepatobiliary disorders :
Liver abnormalities, including hepatocellular injury, cholestasis, jaundice and hepatitis,
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders :
Reddening of the skin, rash, pruritis, exanthema, urticaria
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders :
upus syndrome
Reproductive system and breast disorders :
In some cases a diminution of potency and a drop in sperm count have been observed after high doses of Propafenone. This is reversible when treatment is discontinued.
General disorders and administration site conditions :
Fatigue, chest pain
Investigations :
Elevated liver enzymes (serum transaminases and alkaline phosphatase)
OVERDOSAGE :
The following effects have been selected on the basis of their potential clinical significance (possible signs and symptoms in parentheses where appropriate)-not necessarily inclusive
Acute and/or chronic :
Bradycardia slow heartbeat); hypotension dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting); intra-atrial and intraventricular conduction disturbances ; seizures ; somnolence sleepiness); ventricular arrhythmias
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Treatment is primarily supportive and symptomatic and may include: Defibrillation and infusion of dopamine and isoproterenol to control rhythm and blood pressure; intravenous diazepam for convulsions ; mechanical respiratory assistance and external cardiac massage.
Supportive care :
Patients in whom intentional overdose is confirmed or suspected should be referred for psychiatric consultation.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
PROPAFENONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS 150/300 contains Propafenone Hydrochloride USP 150 mg/300 mg respectively.
3 Strips of 10 Tablets in a carton.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular