5 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
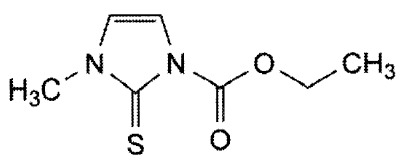
CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. (Carbimazole) is an anti-thyroid substance which depresses the formation of thyroid hormone. Chemically, Carbimazole is Ethyl 3-methyl-2-thioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-imidazole-1-carboxylate. The molecular formula is C7H10N2O2S and molecular weight is 186.2
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. is white coloured, circular, biconvex tablet having breakline on one side and other side plain.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Carbimazole B.P. 5 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTIONS :
Carbimazole is an anti-thyroid substance which depresses the formation of thyroid hormone. It reduces the uptake and concentration of inorganic iodine by the thyroid but its main effect is to reduce the formation of di-iodotyrosine and thyroxine.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Carbimazole is absorbed rapidly from the gastro-intestinal tract and is widely distributed throughout the body. Carbimazole is completely metabolised to methimazole and it is the metabolite that is responsible for its clinical activity. Carbimazole readily crosses the placental barrier and also attains a high concentration in the milk of lactating patients. Excretion in the urine is rapid. The elimination half-life of methimazole may be increased in hepatic and renal impairment.
INDICATIONS :
Carbimazole is an anti-thyroid agent. It is indicated in adults and children in all conditions where reduction of thyroid function is required.
Such conditions are :
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Preparation for thyroidectomy in hyperthyroidism.
- Therapy prior to and post radio-iodine treatment.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION :
Administration :
CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. is for oral administration.
Dosage :
Adults :
The initial dose is in the range 20 – 60 mg and should be titrated against thyroid function until the patient is euthyroid in order to reduce the risk of over-treatment and resultant hypothyroidism. Subsequent therapy may then be administered in one of two ways.
Maintenance regimen : Final dosage is usually in the range 5 – 15 mg per day, which may be taken as a single daily dose. Therapy should be continued for at least six, and up to 18 months. Serial thyroid function monitoring is recommended, together with appropriate dosage modification in order to maintain a euthyroid state.
Blocking-replacement regimen :
Dosage is maintained at the initial level, i.e. 20 – 60 mg per day, and supplemental l-thyroxine, 50 – 150 mcg per day, is administered concomitantly, in order to prevent hypothyroidism. Therapy should be continued for at least six months, and up to eighteen months.
Where a single dosage of less than 20 mg is recommended, it is intended that Carbimazole 5 mg Tablets should be taken.
Elderly :
No special dosage regimen is required, but care should be taken to observe the contraindications and warnings.
Children :
The usual initial daily dose is 15 mg per day.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. is contraindicated in patients with :
- a previous history of adverse reactions to carbimazole or to any of the excipients in the composition.
- serious, pre-existing haematological conditions.
- severe hepatic insufficiency.
CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
Bone marrow depression including neutropenia, eosinophilia, leucopenia and agranulocytosis has been reported. Fatalities with carbimazole-induced agranulocytosis have been reported. Rare cases of pancytopenia/aplastic anaemia and isolated thrombocytopenia have also been reported. Additionally, very rare cases of haemolytic anaemia have been reported. As fatal cases of agranulocytosis with carbimazole have been reported and early treatment of agranulocytosis is essential, it is important that patients should always be warned about the onset of sore throats, bruising or bleeding, mouth ulcers, fever, malaise and should be instructed to stop the drug and to seek medical advice immediately. In such patients, blood cell counts should be performed immediately, particularly where there is any clinical evidence of infection. Early withdrawal of CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. will increase the chance of complete recovery.
Following the onset of any signs and symptoms of hepatic disorder (pain in the upper abdomen, anorexia, general pruritus) in patients, the drug should be stopped and liver function tests performed immediately. CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. should be used with caution in patients with mild-moderate hepatic insufficiency. If abnormal liver function is discovered, the treatment should be stopped. The half-life may be prolonged due to the liver disorder. CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. should be stopped temporarily at the time of administration of radio-iodine. Patients unable to comply with the instructions for use or who cannot be monitored regularly should not be treated with CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. Regular full blood count checks should be carried out in patients who may be confused or have a poor memory.
Precaution should be taken in patients with intrathoracic goitre, which may worsen during initial treatment with CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. Tracheal obstruction may occur due to intrathoracic goitre. The use of carbimazole in non-pregnant women of childbearing potential should be based on individual risk/benefit assessment. There is a risk of cross-allergy between carbimazole, thiamazole, methimazole and propylthiouracil. CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : Category C
Carbimazole crosses the placenta but, provided the mother’s dose is within the standard range and her thyroid status is monitored; there is no evidence of neonatal thyroid abnormalities. Studies have shown that the incidence of congenital malformations is greater in the children of mothers whose hyperthyroidism has remained untreated than in those who have been treated with carbimazole. However, cases of congenital malformations have been observed following the use of carbimazole or its active metabolite methimazole during pregnancy. A causal relationship of these malformations, especially choanal atresia and aplasia cutis congenita (congenital scalp defects), to transplacental exposure to carbimazole and methimazole cannot be excluded.
Therefore, the use of carbimazole in non-pregnant women of childbearing potential should be based on individual risk/benefit assessment. Cases of renal, skull, cardiovascular congenital defects, exomphalos, gastrointestinal malformation, umbilical malformation and duodenal atresia have also been reported. Therefore, carbimazole should be used in pregnancy only when propylthiouracil is not suitable. If carbimazole is used in pregnancy, the dose must be regulated by the patient’s clinical condition. The lowest dose possible should be used, and this can often be discontinued three or four weeks before term, in order to reduce the risk of neonatal complications. The blocking-replacement regimen should not be used during pregnancy since very little thyroxine crosses the placenta in the last trimester.
Nursing mothers :
Carbimazole is excreted in milk and if treatment is continued during lactation the patient should not continue to breast-feed her baby.
Paediatric Use :
Safety and efficacy of carbimazole in children below 2 years of age have not been evaluated systematically. Use of carbimazole in children below 2 years of age is therefore not recommended.
EFFECTS ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
Not known
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Little is known about interactions. Interaction studies have not been performed in paediatric patients. Particular care is required in case of concurrent administration of medication capable of inducing agranulocytosis. Since carbimazole is a vitamin K antagonist, the effect of anticoagulants could be intensified. Additional monitoring of PT/INR should be considered, especially before surgical procedures. The serum levels of theophylline can increase and toxicity may develop if hyperthyroidic patients are treated with antithyroid medications without reducing the theophylline dosage. Co-administration of prednisolone and carbimazole may result in increased clearance of prednisolone. Carbimazole may inhibit the metabolism of erythromycin, leading to reduced clearance of erythromycin. Serum digitalis levels may be increased when hyperthyroid patients on a stable digitalis glycoside regimen become euthyroid; a reduced dosage of digitalis glycosides may be needed. Hyperthyroidism may cause an increased clearance of beta-adrenergic blockers with a high extraction ratio. A dose reduction of beta blockers may be needed when a hyperthyroid patient becomes euthyroid.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Adverse reactions usually occur in the first eight weeks of treatment. The most common minor reactions are nausea, headache, arthralgia, mild gastrointestinal disturbance, skin rashes and pruritus. These reactions are usually self-limiting and may not require withdrawal of the drug.
Paediatric population :
Frequency, type and severity of adverse reactions in children appear to be comparable with those in adults.
Blood and lymphatic system disorders :
Bone marrow depression including neutropenia, eosinophilia, leucopenia and agranulocytosis has been reported. Fatalities with carbimazole-induced agranulocytosis have been reported. Rare cases of pancytopenia/aplastic anaemia and isolated thrombocytopenia have also been reported. Additionally, very rare cases of haemolytic anaemia have been reported. Patients should always be warned about the onset of sore throats, bruising or bleeding, mouth ulcers, fever and malaise and should be instructed to stop the drug and to seek medical advice immediately. In such patients, white blood cell counts should be performed immediately, particularly where there is any clinical evidence of infection. Generalised lymphadenopathy.
Immune system disorders :
Angioedema and multi-system hypersensitivity reactions such as cutaneous vasculitis, liver, lung and renal effects occur.
Endocrine disorders :
Insulin autoimmune syndrome (with pronounced decline in blood glucose level).
Nervous system disorders :
Headache, neuritis, polyneuropathy.
Vascular disorders :
Bleeding.
Gastrointestinal disorders :
Nausea, mild gastrointestinal disturbance. Loss of sense of taste has been observed. Acute salivary gland swelling.
Hepatobiliary disorders :
Hepatic disorders, including abnormal liver function tests, hepatitis, cholestatic hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice and most commonly jaundice, have been reported; in these cases carbimazole tablets should be withdrawn.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders :
Skin rashes, pruritus, urticaria. Hair loss has been occasionally reported. Severe cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in both adult and paediatric patients, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (very rare including isolated reports : severe forms, including generalised dermatitis, have only been described in isolated cases).
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders :
Isolated cases of myopathy have been reported. Patients experiencing myalgia after the intake of carbimazole should have their creatine phosphokinase levels monitored.
General disorders and administration site conditions :
Fever, malaise.
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications :
Bruising.
OVERDOSAGE :
No symptoms are likely from a single large dose. Overdosage or accidental poisoning may result in hypothyroidism and goitre.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
If blood dyscrasias occur, the drug should be immediately withdrawn. Further treatment is symptomatic and supportive.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light. Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
CARBIMAZOLE TABLETS B.P. contains Carbimazole B.P. 5 mg.
10 Blisters of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular