400 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
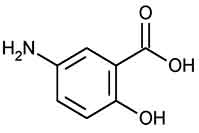
MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP (Mesalamine) is anti-inflammatory drug structurally related to the salicylates and active in inflammatory bowel disease. Chemically, Mesalamine is Benzoic acid, 5-amino-2-hydroxy-. The molecular formula is C7H7NO3 and molecular weight is 153.14.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
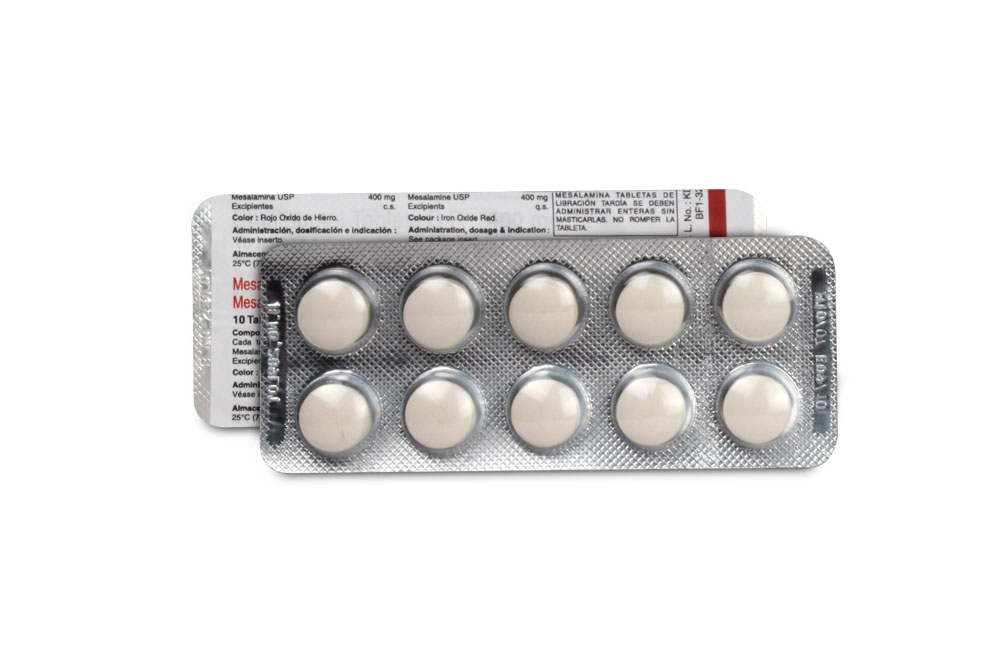
MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP are brown in colour, round, biconvex, filmed coated tablets.
COMPOSITION :
Each film coated tablet contains :
Mesalamine USP 400 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Iron Oxide Red
ACTIONS :
Mesalamine is thought to be the major therapeutically active part of the sulfasalazine molecule in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Sulfasalazine is converted to equimolar amounts of sulfapyridine and mesalamine by bacterial action in the colon. The usual oral dose of sulfasalazine for active ulcerative colitis is 3 to 4 grams daily in divided doses, which provides 1.2 to 1.6 grams of mesalamine to the colon. The mechanism of action of mesalamine (and sulfasalazine) is unknown, but appears to be topical rather than systemic. Mucosal production of arachidonic acid (AA) metabolites, both through the cyclooxygenase pathways, i.e., prostanoids, and through the lipoxygenase pathways, i.e., leukotrienes (LTs) and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids (HETEs), is increased in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease, and it is possible that mesalamine diminishes inflammation by blocking cyclooxygenase and inhibiting prostaglandin (PG) production in the colon.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP are coated with an acrylic-based resin that delays release of mesalamine until it reaches the terminal ileum and beyond. This has been demonstrated in human studies conducted with radiological and serum markers. Approximately 28 % of the mesalamine in MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP is absorbed after oral ingestion, leaving the remainder available for topical action and excretion in the faeces. Absorption of mesalamine is similar in fasted and fed subjects. The absorbed mesalamine is rapidly acetylated in the gut mucosal wall and by the liver. It is excreted mainly by the kidney as N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid.
Mesalamine from orally administered MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP appears to be more extensively absorbed than the mesalamine released from sulfasalazine. Maximum plasma levels of mesalamine and N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid following multiple MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP doses are about 1.5 to 2 times higher than those following an equivalent dose of mesalamine in the form of sulfasalazine. Combined mesalamine and N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid AUCs and urine drug dose recoveries following multiple doses of MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP are about 1.3 to 1.5 times higher than those following an equivalent dose of mesalamine in the form of sulfasalazine.
The t max for mesalamine and its metabolite, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid, is usually delayed, reflecting the delayed release, and ranges from 4 to 12 hours. The half-lives of elimination (t1/2 elm ) for mesalamine and N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid are usually about 12 hours, but are variable, ranging from 2 to 15 hours. There is a large intersubject variability in the plasma concentrations of mesalamine and N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid and in their elimination half-lives following administration of MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP.
INDICATIONS :
MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP are indicated for the treatment of mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis and for the maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis.
Administration :
FOR ORAL ADMINISTRATION.
AS A RULE THE TABLETS ARE SWALLOWED WHOLE WITH A LITTLE LIQUID, INDEPENDENTLY OF MEALS. THE TABLETS MUST NOT BE CHEWED, BITTEN, BROKEN OR DIVIDED.
Dosage :
For the treatment of mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis : The usual dosage in adults is two 400 mg tablets to be taken three times a day for a total daily dose of 2.4 grams for a duration of 6 weeks. For the maintenance of remission of ulcerative colitis : The recommended dosage in adults is 1.6 grams daily, in divided doses. Treatment duration in the prospective, well-controlled trial was 6 months.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Hypersensitivity to mesalazine, any other component of the product, or salicylates. Severe liver and/or renal impairment.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
Most patients who are intolerant or hypersensitive to sulfasalazine are able to take MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP without risk of similar reactions. However, caution is recommended when treating patients allergic to sulfasalazine (risk of allergy to salicylates). Caution is recommended in patients with impaired liver function. The medicine is not recommended for use in patients with renal impairment. The renal function should be regularly monitored (e.g. serum creatinine), especially during the initial phase of treatment. Mesalazine-induced nephrotoxicity should be suspected in patients developing renal dysfunction during treatment. The concurrent use of other known nephrotoxic agents, such as NSAIDs and azothiopirine, may increase the risk of renal reactions. Mesalazine-induced cardiac hypersensitivity reactions (myo- and pericarditis) have been reported rarely. Serious blood dyscrasias have been reported very rarely with mesalazine. Concomitant treatment with mesalazine can increase the risk of blood dyscrasia in patients receiving azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine. Treatment should be discontinued on suspicion or evidence of these adverse reactions.
Pregnancy :
MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP should be used with caution during pregnancy and lactation and only if the potential benefits outweigh the possible hazards in the opinion of the physician. Mesalazine is known to cross the placental barrier, but the limited data available on the use of this compound in pregnant women do not allow assessment of possible adverse effects. No teratogenic effects have been observed in animal studies. Blood disorders (leukopaenia, thrombocytopaenia, anaemia) have been reported in newborns of mothers being treated with MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP.
Nursing mothers :
Mesalazine is excreted in breast milk. The concentration in breast milk is lower than in maternal blood, whereas the metabolite - acetyl-mesalazine - appears in similar or increased concentrations. There is limited experience of the use of oral mesalazine in lactating women. No controlled studies with MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP during breast-feeding have been carried out. Hypersensitivity reactions like diarrhoea in the infant cannot be excluded.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP should not be given with lactulose or similar preparations, which lower stool pH and may prevent release of mesalazine. Concurrent use of other known nephrotoxic agents, such as NSAIDs and azathioprine, may increase the risk of renal reactions.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The side effects are predominantly gastrointestinal, including nausea, diarrhoea and abdominal pain. Headache has also been reported. There have been rare reports of leukopaenia, neutropaenia, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia and thrombocytopaenia, alopecia, peripheral neuropathy, pancreatitis, abnormalities of hepatic function and hepatitis, myocarditis and pericarditis, allergic and fibrotic lung reactions, lupus erythematosus-like reactions and rash (including urticaria), interstitial nephritis and nephrotic syndrome with oral mesalamine treatment, usually reversible on withdrawal. Renal failure has been reported. Mesalamine-induced nephrotoxicity should be suspected in patients developing renal dysfunction during treatment. Mesalamine may very rarely be associated with an exacerbation of the symptoms of colitis, Stevens Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme. Other side effects observed with sulfasalazine such as depression of sperm count and function, have not been reported with MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP.
OVERDOSAGE AND TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Two cases of paediatric overdosage have been reported. A 3-year-old male who ingested 2 grams of MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP was treated with ipecac and activated charcoal; no adverse events occurred. Another 3-year-old male, approximately 16 kg, ingested an unknown amount of a maximum of 24 grams of MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP crushed in solution (i.e., uncoated mesalamine); he was treated with orange juice and activated charcoal, and experienced no adverse events. In dogs, single doses of 6 grams of MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP resulted in renal papillary necrosis but were not fatal. This was approximately 12.5 times the recommended human dose (based on a dose of 2.4 g/day in a 50 kg person). Single oral doses of uncoated mesalamine in mice and rats of 5000 mg/kg and 4595 mg/kg, respectively, or of 3000 mg/kg in cynomolgus monkeys, caused significant lethality.
STORAGE :
Store below 25°C (77°F), protected from moisture and light.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
MESALAMINE DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETS USP contains Mesalamine 400 mg.
10 blisters of 10 tablets per box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular