667 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
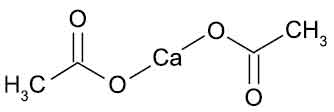
CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP (Calcium Acetate) is a antihyperphosphataemic. Calcium acetate is Acetic acid, calcium salt. The molecular formula is C4H6CaO4 and molecular weight is 158.17
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP is white coloured capsule shaped uncoated tablet.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Calcium Acetate USP 667 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTIONS :
Patients with advanced renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min) exhibit phosphate retention and some degree of hyperphosphataemia. The retention of phosphate plays a pivotal role in causing secondary hyperparathyroidism associated with osteodystrophy, and soft-tissue calcification. The mechanism by which phosphate retention leads to hyperparathyroidism is not clearly delineated. Therapeutic efforts directed toward the control of hyperphosphataemia include reduction in the dietary intake of phosphate, inhibition of absorption of phosphate in the intestine with phosphate binders, and removal of phosphate from the body by more efficient methods of dialysis. The rate of removal of phosphate by dietary manipulation or by dialysis is insufficient. Dialysis patients absorb 40 % to 80 % of dietary phosphorus. Therefore, the fraction of dietary phosphate absorbed from the diet needs to be reduced by using phosphate binders in most renal failure patients on maintenance dialysis. Calcium acetate, when taken with meals, combines with dietary phosphate to form insoluble calcium phosphate which is excreted in the faeces. Maintenance of serum phosphorus below 6.0 mg/dl is generally considered as a clinically acceptable outcome of treatment with phosphate binders.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Calcium acetate is highly soluble at neutral pH, making the calcium readily available for binding to phosphate in the proximal small intestine.
Absorption :
Data from healthy subjects and renal dialysis patients under various conditions indicate that after oral administration of calcium acetate, approximately 40 % is absorbed in the fasting state and approximately 30 % is absorbed in the non-fasting state.
Elimination :
Faecal
INDICATIONS :
CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP is indicated in patients with end-stage renal failure to lower serum phosphate concentrations. It does not promote aluminium absorption.
Administration :
CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP is administered orally.
Dosage :
Most patients require 3 to 4 tablets with each meal.
Usual adult and adolescent dose :
Antihyperphosphataemic :
Oral, 2 tablets three times a day with meals. The dosage may be increased gradually to keep serum phosphate concentrations below 6 mg/dl.
Usual paediatric dose :
Safety and efficacy have not been established.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP is contraindicated in patients with hypocalcaemia.
CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS :
Patients with end stage renal failure may develop hypercalcaemia when given calcium with meals. No other calcium supplements should be given concurrently with CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP. Progressive hypercalcaemia due to overdose of CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP may be severe as to require emergency measures. Chronic hypercalcaemia may lead to vascular calcification, and other soft-tissue calcification. The serum calcium level should be monitored twice weekly during the early dose adjustment period. The serum calcium times phosphate (CaXP) product should not be allowed to exceed 66. Radiographic evaluation of suspect anatomical region may be helpful in early detection of soft tissue calcification.
PRECAUTIONS :
Excessive dosage of CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP induces hypercalcaemia; therefore, early in the treatment during dosage adjustment serum calcium should be determined twice weekly. Should hypercalcaemia develop, the dosage should be reduced or the treatment discontinued immediately depending on the severity of hypercalcaemia. CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP should not be given to patients on digitalis, because hypercalcaemia may precipitate cardiac arrhythmias. CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP therapy should always be started at low dose and should not be increased without careful monitoring of serum calcium. An estimate of daily calcium intake should be made initially and the intake adjusted as needed. Serum phosphorus should also be determined periodically. CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : Teratogenic Effects – Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with calcium acetate tablets. It is not known whether calcium acetate tablets can cause foetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Calcium acetate tablets should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing mothers :
It is not known whether calcium acetate is distributed into breast milk.
Paediatric Use :
No information is available on the relationship of age to the effects of calcium acetate in paediatric patients. Safety and efficacy have not been established.
Geriatric Use :
No information is available on the relationship of age to the effects of calcium acetate in geriatric patients.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
The following drug interactions and/or related problems have been selected on the basis of their potential clinical significance (possible mechanism in parentheses where appropriate) not necessarily inclusive :
Note : Combinations containing any of the following, depending on the amount present, may also interact with this medication.
Calcium :
Calcium containing foods or preparations, including dietary supplements or antacids. Concurrent use may cause hypercalcaemia; dietary calcium should be estimated daily initially and intake adjusted as needed.
Digitalis glycosides :
Concurrent use is not recommended because calcium acetate may cause hypercalcaemia, which could precipitate cardiac arrhythmias
Tetracyclines :
oral Concurrent administration may decrease the bioavailability of tetracyclines.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The following side effects have been selected on the basis of their potential clinical significance (possible signs and symptoms in parentheses where appropriate) not necessarily inclusive :
Those indicating need for medical attention :
Incidence rare
Hypercalcaemia, mild constipation); (loss of appetite; nausea or vomiting); hypercalcaemia, severe confusion); full or partial loss of consciousness); incoherent speech)
Note : Mild hypercalcaemia may be asymptomatic.
Those indicating need for medical attention only if they continue or are bothersome :
Incidence less frequent
Nausea, pruritus (itching)
Note: Pruritus may represent an allergic reaction.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS :
The patient should be informed about compliance with dosage instructions, adherence to instructions about diet and avoidance of the use of non-prescription antacids. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of hypercalcaemia.
OVERDOSAGE :
The following effects have been selected on the basis of their potential clinical significance (possible signs and symptoms in parentheses where appropriate) – not necessarily inclusive : Acute and/or chronic Hypercalcaemia, mild constipation); loss of appetite); nausea and vomiting); hypercalcaemia, severe confusion); full or partial loss of consciousness; incoherent speech)
Note : Mild hypercalcaemia may be asymptomatic. Chronic hypercalcaemia may lead to vascular calcification or other soft-tissue calcification.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Mild hypercalcaemia may be controlled by reducing the dose of calcium acetate or temporarily discontinuing therapy. Calcium acetate therapy should be discontinued in severe hypercalcaemia. To enhance elimination severe hypercalcaemia should be treated by haemodialysis.
Monitoring : If chronic hypercalcaemia develops, radiographic evaluation of the suspected anatomical region may detect soft tissue calcification.
Supportive care : Patients in whom intentional overdose is confirmed or suspected should be referred for psychiatric consultation.
STORAGE :
Store below 25°C (77°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
CALCIUM ACETATE TABLETS USP contains Calcium Acetate USP 667 mg.
3 blisters of 10 tablets in a carton.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular