250 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
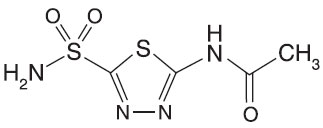
ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP (Acetazolamide) is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Chemically, Acetazolamide is N-(5-Sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide. The molecular formula is C4H6N4O3S2 and molecular weight is 222.25.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP are white coloured, circular, flat tablets with breakline on one side and other side plain.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Acetazolamide USP 250 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTIONS :
Acetazolamide is an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase. By inhibiting the reaction catalysed by this enzyme in the renal tubules, acetazolamide increases the excretion of bicarbonate and of cations, chiefly sodium and potassium, and so promotes alkaline diuresis.
Continuous administration of acetazolamide is associated with metabolic acidosis and resultant loss of diuretic activity. Therefore, the effectiveness of acetazolamide in diuresis diminishes with continuous use. By inhibiting carbonic anhydrase in the eye, acetazolamide decreases intra-ocular pressure and is therefore useful in the treatment of glaucoma.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Acetazolamide is fairly rapidly absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract with peak plasma concentrations occurring about 2 hours after administration by mouth. It has been estimated to have a plasma half-life of about 4 hours. It is tightly bound to carbonic anhydrase and accumulates in tissues containing this enzyme, particularly red blood cells and the renal cortex. It is also bound to plasma proteins. It is excreted unchanged in the urine; renal clearance being enhanced in alkaline urine.
INDICATIONS :
For adjunctive treatment of : oedema due to congestive heart failure; drug-induced oedema; centrencephalic epilepsies (petit mal, unlocalized seizures); chronic simple (open-angle) glaucoma, secondary glaucoma, and preoperatively in acute angle-closure glaucoma where delay of surgery is desired in order to lower intraocular pressure. ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP is also indicated for the prevention or amelioration of symptoms associated with acute mountain sickness in climbers attempting rapid ascent and in those who are very susceptible to acute mountain sickness despite gradual ascent.
Administration :
For Oral Use.
Dosage :
ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP should be used as an adjunct to the usual therapy. The dosage employed in the treatment of chronic simple (openangle) glaucoma ranges from 250 mg to 1 gm of ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP per 24 hours, usually in divided doses for amounts over 250 mg. It has usually been found that a dosage in excess of 1 gm per 24 hours does not produce an increased effect. In all cases, the dosage should be adjusted with careful individual attention both to symptomatology and ocular tension. Continuous supervision by a physician is advisable.
In treatment of secondary glaucoma and in the preoperative treatment of some cases of acute congestive (closed-angle) glaucoma, the preferred dosage is 250 mg every four hours, although some cases have responded to 250 mg twice daily on short-term therapy. In some acute cases, it may be more satisfactory to administer an initial dose of 500 mg followed by 125 mg or 250 mg every four hours depending on the individual case. Intravenous therapy may be used for rapid relief of ocular tension in acute cases. A complementary effect has been noted when ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP has been used in conjunction with miotics or mydriatics as the case demanded.
Epilepsy
It is not clearly known whether the beneficial effects observed in epilepsy are due to direct inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the central nervous system or whether they are due to the slight degree of acidosis produced by the divided dosage. The best results to date have been seen in petit mal in children. Good results, however, have been seen in patients, both children and adults, in other types of seizures such as grand mal, mixed seizure patterns, myoclonic jerk patterns, etc. The suggested total daily dose is 8 to 30 mg per kg in divided doses. Although some patients respond to a low dose, the optimum range appears to be from 375 to 1000 mg daily. However, some investigators feel that daily doses in excess of 1 gm do not produce any better results than a 1 gm dose.
When ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP is given in combination with other anticonvulsants, it is suggested that the starting dose should be 250 mg once daily in addition to the existing medications. This can be increased to levels as indicated above. The change from other medications to ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP should be gradual and in accordance with usual practice in epilepsy therapy.
Congestive Heart Failure
For diuresis in congestive heart failure, the starting dose is usually 250 to 375 mg once daily in the morning (5 mg/kg). If after an initial response, the patient fails to continue to lose oedema fluid, do not increase the dose but allow for kidney recovery by skipping medication for a day. ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP yields best diuretic results when given on alternate days, or for two days alternating with a day of rest. Failures in therapy may be due to overdosage or too frequent dosage. The use of ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP does not eliminate the need for other therapy such as digitalis, bed rest, and salt restriction.
Drug-Induced Oedema
Recommended dosage is 250 to 375 mg of ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP once a day for one or two days, alternating with a day of rest.
Acute Mountain Sickness
Dosage is 500 mg to 1000 mg daily, in divided doses using tablets or sustained-release capsules as appropriate. In circumstances of rapid ascent, such as in rescue or military operations, the higher dose level of 1000 mg is recommended. It is preferable to initiate dosing 24 to 28 hours before ascent and to continue for 48 hours while at high altitude, or longer as necessary to control symptoms.
Note : The dosage recommendations for glaucoma and epilepsy differ considerably from those for congestive heart failure, since the first two conditions are not dependent upon carbonic anhydrase inhibition in the kidney which requires intermittent dosage if it is to recover from the inhibitory effect of the therapeutic agent.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Acetazolamide is contra-indicated in situations in which sodium and/or potassium blood levels are depressed, in cases of marked kidney and liver disease or dysfunction, suprarenal gland failure, and hyperchloremic acidosis. ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP should not be used in patients with hepatic cirrhosis as this may increase the risk of hepatic encephalopathy. Long-term administration of ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP is contraindicated in patients with chronic non-congestive angle-closure glaucoma since it may permit organic closure of the angle to occur while the worsening glaucoma is masked by lowered intraocular pressure. ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP should not be used in patients hypersensitive to sulphonamides.
WARNINGS :
Fatalities have occurred, although rarely, due to severe reactions to sulphonamides including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia, and other blood dyscrasias. Sensitizations may recur when a sulphonamide is readministered irrespective of the route of administration. If signs of hypersensitivity or other serious reactions occur, discontinue use of this drug. Caution is advised for patients receiving concomitant high-dose aspirin and ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP, as anorexia, tachypnoea, lethargy, coma and death have been reported.
PRECAUTIONS :
General :
Increasing the dose does not increase the diuresis and may increase the incidence of drowsiness and/or paraesthesia. Increasing the dose often results in a decrease in diuresis. Under certain circumstances however, very large doses have been given in conjunction with other diuretics in order to secure diuresis in complete refractory failure.
Laboratory Tests :
To monitor for haematologic reactions common to all sulphonamides, it is recommended that a baseline CBC and platelet count be obtained on patients prior to initiating ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP therapy and at regular intervals during therapy. If significant changes occur, early discontinuance and institution of appropriate therapy are important. Periodic monitoring of serum electrolytes is recommended.
Other concomitant conditions :
Both increases and decreases in blood glucose levels have been described in patients treated with acetazolamide. This should be taken into consideration in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus.
Acid/base and electrolyte balance :
Acetazolamide treatment may cause electrolyte imbalances, including hyponatraemia and hypokalaemia, as well as metabolic acidosis. Therefore, periodic monitoring of serum electrolytes is recommended. Particular caution is recommended in patients with conditions that are associated with, or predisposed to, electrolyte and acid/base imbalance, such as patients with impaired renal function (including elderly patients, patients with diabetes mellitus, and patients with impaired alveolar ventilation). (such as patients with pulmonary obstruction or emphysema). In patients with moderate to severe renal impairment, the dose should be reduced by half or the dosage interval should be increased to every 12 hours.
Pregnancy :
Pregnancy Category C
Teratogenic Effects.
Acetazolamide, administered orally or parenterally, has been shown to be teratogenic (defects of the limbs) in mice, rats, hamsters and rabbits. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus.
Nursing mothers :
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Paediatric Use :
The safety and effectiveness of ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP in children have not been established.
EFFECTS ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
Increasing the dose does not increase the diuresis and may increase the incidence of drowsiness and/or paraesthesia. Less commonly, fatigue, dizziness and ataxia have been reported. Disorientation has been observed in a few patients with oedema due to hepatic cirrhosis. Such cases should be under close supervision. Transient myopia has been reported. These conditions invariably subside upon diminution or discontinuance of the medication.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Amphetamines :
By increasing the pH of renal tubular urine, acetazolamide reduces the urinary excretion of amphetamine and so may enhance the magnitude and duration of the effect of amphetamines.
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors :
Because of possible additive effects with other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, concomitant use is not advisable.
Cyclosporine :
When given concomitantly, acetazolamide may elevate cyclosporine blood levels. Caution is advised when administering acetazolamide in patients receiving cyclosporine.
Folic Acid Antagonists :
Acetazolamide may potentiate the effects of other folic acid antagonists.
Hypoglycaemics Agents :
Both increases and decreases in blood glucose levels have been described in patients treated with acetazolamide. This should be taken into consideration in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus treated with antidiabetic agents.
Lithium :
Acetazolamide increases lithium excretion due to impaired reabsorption of lithium in the proximal tubule. The effect of lithium carbonate may be decreased.
Methenamine compounds :
By increasing the pH of urine, acetazolamide may prevent the urinary antiseptic effect of methenamine compounds.
Phenytoin :
When given concomitantly, acetazolamide modifies the metabolism of phenytoin, leading to increased serum levels of phenytoin. Acetazolamide may increase the occurrence, or accelerate the manifestation of osteomalacia in some patients receiving chronic phenytoin therapy. Caution is advised in patients receiving chronic concomitant therapy.
Primidone :
By decreasing the gastrointestinal absorption of primidone, acetazolamide may decrease serum concentrations of primidone and its metabolites, with a consequent possible decrease in anticonvulsant effect. Caution is advised when beginning, discontinuing, or changing the dose of acetazolamide in patients receiving primidone.
Quinidine :
By increasing the pH of renal tubular urine, acetazolamide reduces the urinary excretion of quinidine and so may enhance the effect of quinidine.
Salicylates :
Caution is advised for patients receiving concomitant aspirin and acetazolamide, as severe toxicity has been reported. Severe metabolic acidosis has been reported in patients with normal renal function during treatment with acetazolamide and salicylates.
Pharmacokinetic studies showed that the plasma protein binding and renal clearance of acetazolamide were significantly reduced during chronic salicylate therapy. Systemic acidosis produced by acetazolamide may increase salicylate toxicity by enhancing salicylate tissue penetration. Precaution is advised for patients receiving concomitant high-dose aspirin and ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP as anorexia, tachypnoea, lethargy and coma have been reported due to a possible drug interaction. Concomitant administration with high-dose aspirin may potentiate the adverse reactions of ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP.
Sodium Bicarbonate :
The use of concurrent sodium bicarbonate therapy enhances the risk of renal calculus formation in patients taking acetazolamide.
Cardiovascular Agents :
Potentiation of the effects of oral anticoagulants is possible when administered with ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP, and may warrant a reduction in the dose of the anticoagulant. Adjustment of dose may be required when ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP is given with cardiac glycosides or antihypertensive agents.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Side effects during short-term therapy are usually non-serious. Those effects which have been noted include : paraesthesia, particularly a “tingling” feeling in the extremities; some loss of appetite; taste disturbance, polyuria, flushing, thirst, headache, dizziness, fatigue, irritability, depression, reduced libido and occasional instances of drowsiness and confusion. Rarely, photosensitivity has been reported. During long-term therapy, metabolic acidosis and electrolyte imbalance may occasionally occur. This can usually be corrected by the administration of bicarbonate. Transient myopia has been reported. This condition invariably subsides upon diminution or withdrawal of the medication.
Gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea.
ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP is a sulphonamide derivative and therefore some side-effects similar to those caused by sulphonamides have occasionally been reported. These include fever, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytic purpura, leucopenia, and aplastic anaemia, bone marrow depression, pancytopenia, rash (including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis), anaphylaxis, crystalluria, calculus formation, renal and ureteral colic, and renal lesions. Rarely, fulminant hepatic necrosis has been reported. Other occasional adverse reactions include : urticaria, melaena, haematuria, glycosuria, impaired hearing and tinnitus, abnormal liver function, renal failure and rarely, hepatitis or cholestatic jaundice, flaccid paralysis, and convulsions.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS :
Adverse reactions common to all sulphonamide derivatives may occur : anaphylaxis, fever, rash (including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis) crystalluria, renal calculus, bone marrow depression, thrombocytopenic purpura, haemolytic anaemia, leucopenia, pancytopenia and agranulocytosis. Precaution is advised for early detection of such reactions and the drug should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. In patients with pulmonary obstruction or emphysema where alveolar ventilation may be impaired, ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP, which may precipitate or aggravate acidosis should be used with caution.
Gradual ascent is desirable to try to avoid acute mountain
sickness. If rapid ascent is undertaken and ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP is used, it should be noted that such use does not obviate the need for prompt descent if severe forms of high altitude sickness occur. i.e., high altitude pulmonary oedema (HAPE) or high-altitude cerebral oedema. Caution is advised for patients receiving concomitant high-dose aspirin and ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP, as anorexia, tachypnoea, lethargy, coma and death have been reported.
OVERDOSAGE AND TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
No data are available regarding acetazolamide overdose in humans as no cases of acute poisoning with this drug have been reported. Animal data suggest that acetazolamide is remarkably nontoxic. No specific antidote is known. Treatment should be symptomatic and supportive. Electrolyte imbalance, development of an acidotic state, and central nervous effects might be expected to occur. Serum electrolyte levels (particularly potassium) and blood pH levels should be monitored. Supportive measures are required to restore electrolyte and pH balance. The acidotic state can usually be corrected by the administration of bicarbonate. Despite its high intraerythrocytic distribution and plasma protein binding properties, ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP may be dialyzable. This may be particularly important in the management of ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP overdosage when complicated by the presence of renal failure.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
ACETAZOLAMIDE TABLETS USP contains Acetazolamide USP 250 mg.
10 Blisters of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular