500 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
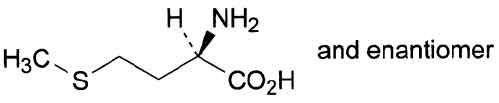
DL-Methionine TABLETS (DL-Methionine) is an essential amino acid that plays a vital role in intermediatary metabolism. Chemically, DL-Methionine is (2RS)-2-amino-4-(methylsulphanyl) butanoic acid. The molecular formula is C5H11NO2S and molecular weight is 149.2
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
DL-Methionine TABLETS are orange coloured, elongated, biconvex, film-coated tablets, breakline on one side & plain on other side.
COMPOSITION :
Each film-coated tablet contains :
DL-Methionine B.P. 500 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Sunset Yellow FCF Supra.
Flavour : Strawberry.
Each film-coated tablet contains :
DL-Methionine B.P. 250 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Sunset Yellow FCF Supra.
Flavour : Strawberry.
ACTION :
Acidifier, urinary : DL-Methionine produces ammonia-free urine by lowering the urinary pH. Antidote, to acetaminophen overdose : DL-Methionine may protect against acetaminophen overdose-induced hepatotoxicity by maintaining or restoring hepatic concentrations of glutathione. Glutathione is required to inactivate an intermediate metabolite of acetaminophen, which is hepatotoxic. In acetaminophen overdose, excessive quantities of this metabolite are formed because the primary metabolic pathways (glucuronide and sulfate conjugation) become saturated. The excess metabolite binds irreversibly to essential hepatic proteins and enzymes, causing cell damage and death. DL-Methionine serves as a precursor for the synthesis of glutathione and sulfate.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Absorption : DL-Methionine is absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract. Absorption is unpredictable in patients who are vomiting.
Half-Life : Not known.
Distribution : Not known.
Metabolism : DL-Methionine is metabolised via s-adenosylMethionine to homocysteine. About 80% is further converted to cystathionine, cysteine, taurine and inorganic sulphate.
Excretion : DL-Methionine is excreted in the urine as an inorganic sulphate.
INDICATIONS :
Dermatitis, contact (treatment) and Urine odour : DL-Methionine is indicated for the treatment of dermatitis and ulcerations, and for the control of urine odour, caused by ammoniacal urine in incontinent adults. DL-Methionine is also indicated in infants for the treatment of diaper rash. Toxicity, acetaminophen (treatment) : DL-Methionine may be used in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose to protect against hepatotoxicity. However, oral N-acetylcysteine is considered the treatment of choice for acetaminophe overdose. Use of DL-Methionine should be limited to emergency situations in which N-acetylcysteine is not available.
Administration :
DL-Methionine TABLETS are for oral administration.
Dosage :
Usual adult and adolescent dose
Acidifier, urinary :
Oral, 500 mg three or four times a day. Each dose should be taken with a meal.
Antidote, to acetaminophen overdose :
Oral, 2.5 gm every four hours, up to a total dose of 10 gm. The first dose must be given within eight to twelve hours after the toxic ingestion.
Usual paediatric dose
Antidote, to acetaminophen overdose :
Children 12 years of age or older : Oral, 2.5 gm every four hours, up to a total dose of 10 gm. The first dose must be given within eight to twelve hours after the toxic ingestion.
Children 3 to 11 years of age : Oral, 1 gm every four hours, up to a total dose of 4 gm. The first dose must be given within eight to twelve hours after the toxic ingestion.
Children up to 3 years of age : Dosage has not been established.
General Dosing Information :
For treatment of contact dermatitis
If there is no improvement after 10 days of therapy, it is recommended that DL-Methionine be discontinued because the probable cause of the rash is something other than ammoniacal urine.
For treatment of acetaminophen toxicity
Oral N-acetylcysteine is considered the treatment of choice for acetaminophen overdose. Use of DL-Methionine should be limited to emergency situations in which N-acetylcysteine is not available. Patients with suspected acetaminophen overdose should receive supportive therapy. This may include establishing and maintaining adequate airway, respiratory, and circulatory function; maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance; correcting hypoglycemia; and administering vitamin K1 (if prothrombin time ratio exceeds 1.5) and fresh frozen plasma or prothrombin complex concentrate (if prothrombin time ratio exceeds 3). Gastric decontamination, by means of lavage or ipecac-induced emesis may be beneficial if carried out within 4 hours after ingestion of potentially toxic doses of acetaminophen.
Administration of activated charcoal following acetaminophen overdose is controversial. Activated charcoal effectively adsorbs acetaminophen, but also adsorbs DL-Methionine, thereby diminishing the antidotal effectiveness of both agents.
Additional therapy to treat mixed overdose with other agents (i.e., naloxone for an opioid analgesic) may be needed, especially if symptoms of central nervous system (CNS) depression occur within a few hours after ingestion of potentially toxic doses of acetaminophen.
DL-Methionine therapy must be instituted within 8 to 12 hours after acetaminophen ingestion. If given more than 15 hours postingestion, DL-Methionine may precipitate hepatic encephalopathy. It is recommended that DL-Methionine be administered as soon as possible after ingestion of an overdose is suspected, without waiting for the results of plasma acetaminophen concentrations or other laboratory tests. Plasma acetaminophen concentration should be determined not less than 4 hours following ingestion of the overdose. Concentrations determined prior to this time are not reliable for assessing potential hepatotoxicity. The following chart, derived from the Rumack-Matthew nomogram, may be used to predict which patients may develop hepatotoxicity when the time of ingestion. If the initial determination indicates a plasma concentration below those listed at the times indicated, cessation of antidotal therapy can be considered.
Diet/Nutrition
For treatment of contact dermatitis :
It is essential that adequate protein intake be maintained during therapy with DL-Methionine and that the recommended dosage of medication not be exceeded. Excessive dosages of DL-Methionine added alone to the diet over an extended period of time may result in lower than normal weight gain in infants, when protein intake is insufficient.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
DL-Methionine should not be used for the treatment of Paracetamol overdosage if more than 10 hours have elapsed since the time of the overdose.
Do not use in patients with metabolic acidosis.
DL-Methionine TABLETS contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS :
Use DL-Methionine with care in patients with established liver disease as hepatic encephalopathy may be precipitated.
PRECAUTIONS :
Use with caution in patients with schizophrenia as daily DL-Methionine dose of 10 to 20 gm have been reported to precipitate acute exacerbation of symptoms in such patients.
DL-Methionine TABLETS should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
The safety, in human pregnancy or during lactation, of the ingestion of higher levels of DL-Methionine than would normally be encountered in the diet, has not been established. DL-Methionine should only be used during pregnancy or lactation if the benefit of its use has been weighed against any potential risks.
EFFECT ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
Patients should be advised that DL-Methionine may cause drowsiness and their ability to drive or operate machinery may be affected.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
The anti-parkinsonism effect of levodopa may be reduced by DL-Methionine, especially if large doses of DL-Methionine are given. DL-Methionine may be adsorbed by activated charcoal and the effect of oral DL-Methionine may be reduced if they are given together .It is recommended that activated charcoal should be cleared from the stomach or avoided if DL-Methionine is to be used.
SIDE EFFECTS :
DL-Methionine may cause nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, and irritability. It should not be used in patients with acidosis. DL-Methionine may aggravate hepatic encephalopathy in patients with established liver damage; it should be used with caution in patients with severe liver disease.
OVERDOSAGE :
Overdosage with DL-Methionine may be associated with the appearance of the above mentioned side effects (nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, irritation).
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
No specific recommendations for treatment of overdose are available. General support measures may be appropriate.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
DL-Methionine TABLETS contain DL-Methionine 500 mg. 100 tablets are packed in a bottle.
DL-Methionine TABLETS contain DL-Methionine 250 mg. 100 tablets are packed in a bottle.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular