250 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
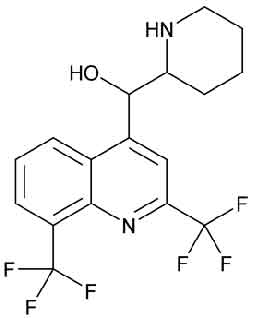
MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP is a 4-methanolquinoline anti-malarial related to quinine. It is a blood schizontocide effective against all forms of malaria including chloroquine- or multidrug-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum. Chemically, Mefloquine Hydrochloride is 4-Quinolinemethanol, α-2-piperidinyl-2,8-bis(trifluoromethyl)-, monohydrochloride,(R*,S*)-. The molecular formula is C17H16F6N2O•HCl and molecular weight is 414.77.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP is white to off-white coloured, circular, biconvex film coated tablet.
COMPOSITION :
Each film coated tablet contains :
Mefloquine Hydrochloride USP 250 mg
Excipients .........................................q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide B.P.
ACTIONS :
MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP acts on the asexual in traerythrocytic forms of the human malaria parasites : Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. malariae and P. ovale MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP is effective against malaria parasites resistant to other Antimalerial such as chloroquine, proguanil, pyrimethamine and pyrimet hamine-sulfonamide combinations.
Microbiology :
Activity In Vitro and In Vivo
Mefloquine is active against the erythrocytic stages of Plasmodium species . However, the drug has no effect against the exoerythrocytic (hepatic) stages of the parasite. Mefloquine is effective against malaria parasites resistant to chloroquine. Drug Resistance Strains of P. falciparum with decreased susceptibility to mefloquine can be selected in vitro or in vivo. Resistance of P. falciparum to mefloquine has been reported in areas of multi-drug resistance in South East Asia. Increased incidences of resistance have also been reported in other parts of the world.
Cross-Resistance
Cross-resistance between mefloquine and halofantrine and cross-resistance between mefloquine and quinine have been observed in some regions.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Absorption :
The absolute oral bioavailability of mefloquine has not been determined since an intravenous formulation is not available. The bioavailability of the tablet formation compared with an oral solution was over 85 %. The presence of food significantly enhances the rate and extent of absorption, leading to about a 40 % increase in bioavailability. Plasma concentrations peak 6 to 24 hours (median, about 17 hours) after a single dose of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP. Maximum plasma concentrations in µg/l are roughly
equivalent to the dose in milligrams (for example, a single 1000 mg dose produces a maximum concentration of about 1000 µg/l). At a dose of 250 mg once weekly produces maximum steady-state plasma concentrations of 1000 to 2000 µg/l, which are reached after 7 to 10 weeks.
Distribution :
In healthy adults, the apparent volume of distribution is approximately 20 l/kg, indicating extensive tissue distribution. Mefloquine may accumulate in parasitized erythrocytes. -to-plasma concentration ratio of about 2. Protein binding is about 98 %. Mefloquine blood concentration of 620 ng/mL are considered necessary to achieve 95 % prophylactic efficacy. Mefloquine crosses the placenta. Excretion into breast milk appears to be minimal.
Metabolism :
Mefloquine is extensively metabolised in the liver by the cytochrome P450 system. In vitro and in vivo studies strongly suggested that CYP3A4 is the major is form involved. Two metabolites of mefloquine have been identified in humans. The main metabolite, 2,8- bis -trifluoromethyl-4-quinoline carboxylic acid, is inactive in P. falciparum . In a study in healthy volunteers, the carboxylic acid metabolite appeared in plasma 2 to 4 hours after a single oral dose. Maximum plasma concentrations of the metabolite, which were about 50 % higher than those of mefloquine, were reached after 2 weeks. Thereafter, plasma levels of the main metabolite and mefloquine declined at a similar rate. The area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of the main metabolite was 3 to 5 times larger than that of the parent compound. The other metabolite, an alcohol, was present in minute quantities only.
Elimination :
In several studies in healthy adults, the mean elimination half-life of mefloquine varied between 2 and 4 weeks, with an average of about 3 weeks. Total clearance, which is essentially hepatic, is in the order of 30 ml/min. There is evidence that mefloquine is excreted mainly in the bile and faeces. In volunteers, urinary excretion of unchanged mefloquine and its main metabolite accounted for about 9 % and 4 % of the dose, respectively. Concentrations of other metabolites could not be measured in the urine.
Administration :
Mefloquine has a bitter and slightly burning taste. MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should be swallowed whole, with at least one glass of liquid. The tablets may be crushed and suspended in a small amount of water, milk or other beverage for administration to small children and other persons unable to swallow them whole.
Prophylaxis standard dosage
The recommended prophylactic dose of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP is approximately 5 mg/kg bodyweight once weekly :
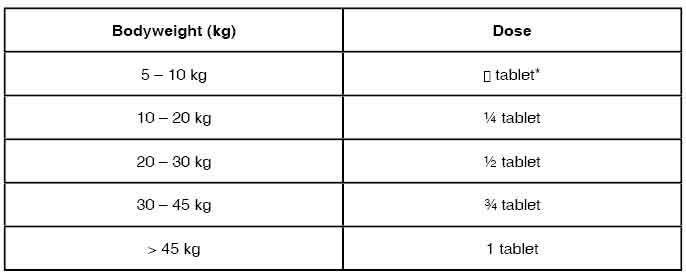
*Approximate tablet fraction based on a dosage of 5 mg/kg bodyweight. Exact doses for children weighing less than 10 kg may best be prepared and dispensed by pharmacists. Weekly doses should be taken regularly, always on the same day of each week, preferably after the main meal. The first dose should be taken at least one week before arrival in an endemic area. Experience with MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP in infants less than 3 months old or weighing less than 5 kg is limited. The dosage for children has been extrapolated from the recommended adult dose.
Special dosage instructions
Prophylaxis
For last-minute travellers to high-risk areas, if the start of prophylaxis one week before arrival in the endemic area is not possible, a ”loading dose” administration, consisting of the weekly dosage administered daily for three consecutive days followed, thereafter, by standard weekly dosing, is recommended :
Day 1 1st Dose
Day 2 2nd Dose
Day 3 3rd Dose
Thereafter Regular Weekly Dosed
The use of a loading dose may be associated with an increased incidence of adverse events. In certain cases, e.g. when a traveller is taking other medication, it may be desirable to start prophylaxis 2 to 3 weeks prior to departure, in order to ensure that the combination of medicines is well tolerated. To reduce the risk of malaria after leaving an endemic area, prophylaxis must be continued for 4 additional weeks to ensure suppressive blood levels of the medicine when merozoites emerge from the liver. When prophylaxis with MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP fails, physicians should carefully evaluate which Antimalerial to use for therapy. Regarding the use of halofantrine, see Warnings and Precautions; and Interactions with Other Medicinal Products and Other Forms of Interactions.
Therapy
For partially immune individuals, i.e. for inhabitants of malarious endemic areas, a reduced dose may be adequate. A second full dose should be given to patients who vomit less than 30 minutes after receiving MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP. If vomiting occurs 30 to 60 minutes after a dose, an additional half-dose should be given. After treatment of P. vivax malaria, relapse prophylaxis with an 8-aminoquinoline derivative (e.g. primaquine) should be considered in order to eliminate liver forms. If a full treatment course with MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP does not lead to improvement within 48 to 72 hours, MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should not be used for retreatment. An alternative therapy should be used. When breakthrough malaria occurs during MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP prophylaxis, physicians should carefully evaluate which antimalerial to use for therapy.
MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP can be given for severe acute malaria after an initial course of intravenous quinine lasting at least 2 – 3 days. Interactions leading to adverse events can largely be prevented by allowing an interval of at least 12 hours after the last dose of quinine. In areas with multiresistant malaria, initial treatment with artemisinin or a derivative, if available, followed by MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP is also an option.
Stand-by treatment
MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP may be prescribed for use as stand-by medication when prompt medical attention is unavailable within 24 hours of onset of symptoms. Self-treatment should be started with a dose of about 15 mg/kg; for patients weighing 45 kg or more the initial dose would thus be 3 MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP. If it will not be possible to obtain professional medical care within 24 hours, and no severe side-effects occur, a second fraction of the total therapeutic dosage should be taken 6 – 8 hours later (2 tablets in patients weighing 45 kg or more). Patients weighing more than 60 kg should take an additional tablet 6 – 8 hours after the second dose. Patients should be advised to consult a physician as soon as possible after self-treatment, even if they feel they have fully recovered to confirm or reject the presumptive diagnosis.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Use of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to mefloquine or related compounds (eg, quinine and quinidine) or to any of the excipients contained in the formulation. Mefloquine Hydrochloride Tablets should not be prescribed for prophylaxis in patients with active depression, a recent history of depression, generalized anxiety disorder, psychosis, or schizophrenia or other major psychiatric disorders, or with a history of convulsions. MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS :
In case of life-threatening, serious or overwhelming malaria infections due to P. falciparum, patients should be treated with an intravenous Antimalerial drug. Following completion of intravenous treatment, Mefloquine Hydrochloride Tablets may be given to complete the course of therapy. Data on the use of halofantrine subsequent to administration of Mefloquine Hydrochloride Tablets suggest a significant, potentially fatal prolongation of the QTc interval of the ECG. Therefore, halofantrine must not be given simultaneously with or subsequent to Mefloquine Hydrochloride Tablets. No data are available on the use of Mefloquine Hydrochloride Tablets after halofantrine. Mefloquine may cause psychiatric symptoms in a number of patients, ranging from anxiety, paranoia, and depression to hallucinations and psychotic behaviour. On occasions, these symptoms have been reported to continue long after mefloquine has been stopped. Rare cases of suicidal ideation and suicide have been reported though no relationship to drug administration has been confirmed. To minimize the chances of these adverse events, mefloquine should not be taken for prophylaxis in patients with active depression or with a recent history of depression, generalized anxiety disorder, psychosis, or schizophrenia or other major psychiatric disorders. Mefloquine Hydrochloride Tablets should be used with caution in patients with a previous history of depression.
During prophylactic use, if psychiatric symptoms such as acute anxiety, depression, restlessness or confusion occur, these may be considered prodromal to a more serious event. In these cases, the drug must be discontinued and an alternative medication should be substituted. Concomitant administration of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP and quinine or quinidine may produce electrocardiographic abnormalities. Concomitant administration of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP and quinine or chloroquine may increase the risk of convulsions.
PRECAUTIONS :
MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : Pregnancy Category C
Mefloquine has been demonstrated to be teratogenic in rats and mice at a dose of 100 mg/kg/day. In rabbits, a high dose of 160 mg/kg/day was embryotoxic and teratogenic, and a dose of 80 mg/kg/day was teratogenic but not embryotoxic. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. However, clinical experience with MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP has not revealed an embryotoxic or teratogenic effect. Mefloquine should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Women of childbearing potential who are travelling to areas where malaria is endemic should be warned against becoming pregnant. Women of childbearing potential should also be advised to practice contraception during malaria prophylaxis with MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP and for up to 3 months thereafter. However, in the case of unplanned pregnancy, malaria chemoprophylaxis with MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP is not considered an indication for pregnancy termination.
Nursing mothers :
Mefloquine is excreted in human milk in small amounts, the activity of which is unknown. Based on a study in a few subjects, low concentrations (3 % to 4 %) of mefloquine were excreted in human milk following a dose equivalent to 250 mg of the free base. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from mefloquine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Paediatric Use :
Use of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP to treat acute, uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in paediatric patients is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP in adults with additional data from published open-label and comparative trials using MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP to treat malaria caused by P. falciparum in patients younger than 16 years of age. The safety and effectiveness of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP for the treatment of malaria in paediatric patients below the age of 6 months have not been established.
In several studies, the administration of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP for the treatment of malaria was associated with early vomiting in paediatric patients. Early vomiting was cited in some reports as a possible cause of treatment failure. If a second dose is not tolerated, the patient should be monitored closely and alternative malaria treatment considered if improvement is not observed within a reasonable period of time.
EFFECT ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
Persons experiencing dizziness and loss of balance or other disorders of the central or peripheral nervous system should be cautious with regard to driving, piloting aircraft, operating machinery, deep-sea diving, or other activities requiring alertness and fine motor coordination. In a small number of patients it has been reported that dizziness or vertigo and loss of balance may continue for months after discontinuation of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP.
INTERACTION AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Interactions with other Medicinal Products and other Forms of Interaction :
Concomitant administration of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP and other related compounds (e.g. quinine, quinidine and chloroquine) may produce electrocardiographic abnormalities and increase the risk of convulsions . There is evidence that the use of halofantrine during MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP therapy for prophylaxis or treatment of malaria, or within 15 weeks of the last dose of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP causes a significant lengthening of the QTc interval. Due to increased plasma concentrations and elimination half-life of mefloquine following co-administration with ketoconazole, the risk of QTc prolongation may also be expected if ketoconazole is taken during MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP therapy for prophylaxis or treatment of malaria or within 15 weeks after the last dose of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP.
Clinically significant QTc prolongation has not been found with mefloquine alone. This appears to be the only clinically relevant interaction of this kind with MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP, although theoretically co-administration of other medicines known to alter cardiac conduction (e.g. anti-arrhythmic or β-adrenergic blocking agents, calcium channel blockers, antihistamines or H1-blocking agents, tricyclic antidepressants and phenothiazines) might also contribute to a prolongation of the QTc interval. There are no data that conclusively establish whether the concomitant administration of mefloquine and the above-listed agents has an effect on cardiac function.
In patients taking an anticonvulsant (e.g. valproic acid, carbamazepine, phenobarbital or phenytoin), the concomitant use of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP may reduce seizure control by lowering the plasma levels of the anticonvulsant. Dosage adjustments of antiseizure medication may be necessary in some cases. When MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP is taken concurrently with oral live typhoid vaccines, attenuation of immunization cannot be excluded. Vaccinations with attenuated live bacteria should therefore be completed at least 3 days before the first dose of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP .No other medicine interactions are known. Nevertheless, the effects of MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP on travellers receiving concomitant medication, particularly diabetics or patients using anticoagulants, should be checked before departure.
Other potential interactions :
Mefloquine does not inhibit or induce the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. It is therefore not expected that the metabolism of medicines given concomitantly with mefloquine is affected. However, inhibitors of the isoenzyme CYP3A4 may modify the pharmacokinetics/metabolism of mefloquine, leading to an increase in mefloquine plasma concentrations and potential risk of adverse reactions. Therefore, mefloquine should be used with caution when administered concomitantly with CYP3A4 inhibitors.Similarly, inducers of the isoenzyme CYP3A4 may modify the pharmacokinetics/metabolism of mefloquine, leading to a decrease in mefloquine plasma concentrations.
Inhibitors of CYP3A4
One pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers showed that the co-administration of ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4, increased the plasma concentrations and elimination half -life of mefloquine.
Inducers of CYP3A4
The long - term use of rifampicin, a potent inducer of CYP3A4, reduced the plasma concentrations and elimination half - life of mefloquine.
Substrates and inhibitors of P-glycoprotein
It has been shown in vitro that mefloquine is a substrate and an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein. Therefore, interactions could also occur with medicines that are substrates or are known to modify the expression of this transporter. The clinical relevance of these interactions are
unknown to date.
Laboratory Tests
Periodic evaluation of hepatic function should be performed during prolonged prophylaxis.
Laboratory
The most frequently observed laboratory alterations which could be possibly attributable to drug administration were decreased haematocrit, transient elevation of transaminases, leucopoenia and thrombocytopenia. These alterations were observed in patients with acute malaria who received treatment doses of the drug and were attributed to the disease itself. During prophylactic administration of mefloquine to indigenous populations in malaria-endemic areas, the following occasional alterations in laboratory values were observed: transient elevation of transaminases, leukocytosis or thrombocytopenia. Because of the long half-life of mefloquine, adverse reactions to mefloquine may occur or persist up to several weeks after discontinuation of the drug.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Mefloquine is well tolerated and rarely has been associated with serious adverse effects when used for prophylaxis. Serious side effects are more frequent with the higher doses of mefloquine used in the treatment of malaria . However, serious side effects of mefloquine may be difficult to distinguish from the symptoms of acute malaria infection Although mefloquine is well tolerated when used for prophylaxis, monitoring the occurrence of severe adverse reactions is important because such reactions are possible .Therefore, patients who experience serious adverse reactions following a prophylactic dose of mefloquine should consult their physician. Ocular lesions were observed in rats fed mefloquine daily for 2 years .These lesions were characterized by retinal degeneration, opacity of the lens, and retinal edema The following side/adverse effects have been selected on the basis of their potential clinical significance (possible signs and symptoms in parentheses where appropriate) ¾ not necessarily inclusive :
Those indicating need for medical attention
Incidence less frequent
Abnormal dreams; asthenia (unusual tiredness or weakness); forgetfulness hypertension (dizziness; severe or continuing headache); hypotension (unusual tiredness or weakness, severe); insomnia (trouble in sleeping).
Incidence rare
Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat); cardiopulmonary arrest (swelling of ankles, feet, and/or lower legs; shortness of breath and/or wheezing); central nervous system (CNS) disturbances or neuropsychiatric toxicity (anxiety; confusion; depression; hallucinations; psychotic
manifestations, such as mood or mental changes, mental depression, and/or restlessness); convulsions encephalopathy (confusion; headache, severe or continuing; irritability; stiff neck; vomiting); erythema multiforme and/or Stevens-Johnson syndrome (aching joints and muscles; blistering, loosening, peeling, or redness of skin; chills, fever, and/or sore throat; red or irritated eye; sores, ulcers, and/or white spots in mouth or on lips; unusual tiredness or weakness); leucopenia (cough or hoarseness; fever or chills; lower back or side pain; painful or difficult urination); thrombocytopenia (unusual bleeding or bruising; black, tarry stools; pinpoint red spots on skin)
How should I store mefloquine?
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light. Safely throw away medicine that is out of date or no longer needed. Keep mefloquine and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of mefloquine.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use mefloquine for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give mefloquine to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about mefloquine. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about mefloquine that is written for health professionals.
OVERDOSAGE :
In cases of over dosage with MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP the symptoms mentioned under Undesirable Effects may be more pronounced.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Patients should be managed by symptomatic and supportive care following MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP overdose. There are no specific antidotes. Monitor cardiac function (if possible by ECG) and euro psychiatric status for at least 24 hours. Provide symptomatic and intensive supportive treatment as required, particularly for cardiovascular disturbances.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
MEFLOQUINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS USP contains Mefloquine Hydrochloride USP 250 mg.
1 Blister of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular