200 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
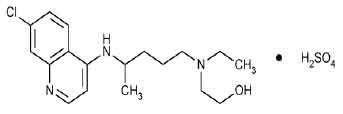
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP (Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate) is a 4-aminoquinoline antimalarial used in the treatment and prophylaxis of malaria. Chemically, Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate is (±)-2-[[4-[(7-Chloro-4-uinolyl) amino]pentyl]ethylamino] ethanol sulfate (1:1) (salt).The molecular formula is C18H26ClN3O • H2SO4 and the molecular weight is 433.95.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
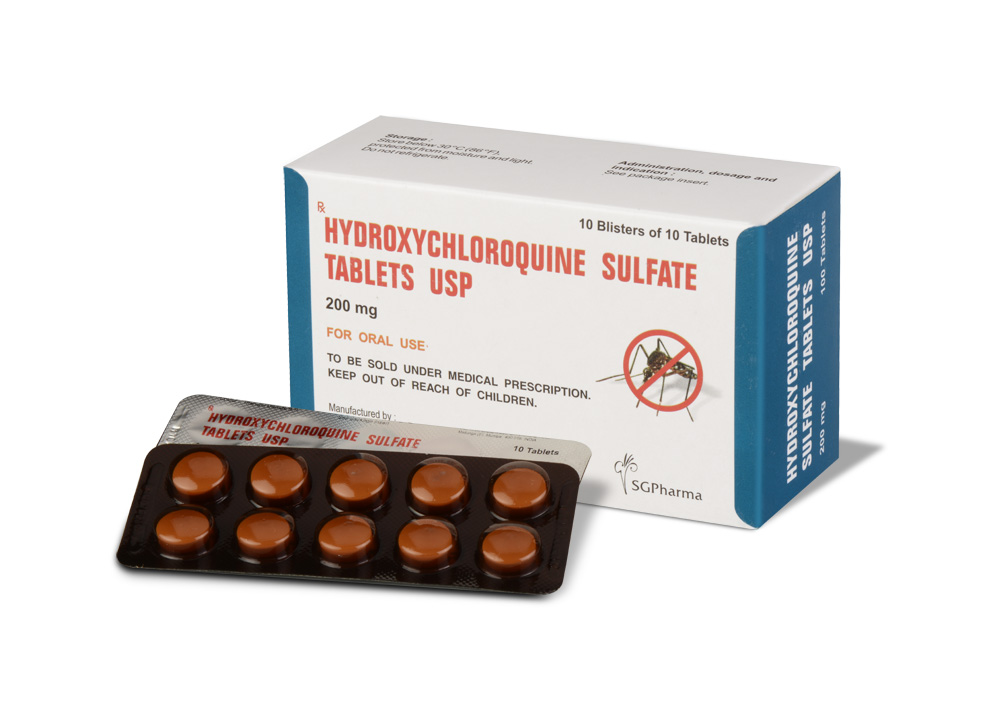
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP are white coloured, circular, biconvex film coated tablets.
COMPOSITION :
Each film coated tablet contains :
Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate USP 200 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide B.P.
ACTIONS :
Hydroxychloroquine may interfere with parasitic nucleoprotein (DNA/RNA) synthesis and parasite growth or cause lysis of parasite or infected erythrocytes. In rheumatoid arthritis, may suppress formation of antigens responsible for symptom-producing hypersensitivity reactions.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Hydroxychloroquine has actions, pharmacokinetics and metabolism similar to those of chloroquine. Following oral administration, hydroxychloroquine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed. In one study, mean peak plasma hydroxychloroquine concentrations following a single dose of 400 mg in healthy subjects ranged from 53-208 ng/ml with a mean of 105 ng/ml. The mean time to peak plasma concentration was 1.83 hours. The mean plasma elimination half-life varied, depending on the post-administration period, as follows; 5.9 hours (at C max- 10 hours), 26.1 hours (at 10-48 hours) and 229 hours (at 48-504 hours). The parent compound and metabolites are widely distributed in the body and elimination is mainly via the urine, where 3 % of the administered dose was recovered over 24 hours in one study.
INDICATIONS :
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP is indicated for Prophylaxis and treatment of acute attacks of malaria due to Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale, and susceptible strains of Plasmodium falciparum. Treatment of chronic discoid and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and acute or chronic rheumatoid arthritis in patients not responding to other therapies.
Administration :
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP are for oral administration.
Dosage :
Rheumatoid Arthritis :
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP is cumulative in action and will require several weeks to exert its beneficial therapeutic effects, whereas minor side effects may occur relatively early. Several months of therapy may be required before maximum effects can be obtained. Initial dosage : In adults, a suitable initial dosage is from 400 to 600 mg daily, preferably taken at meal times. In a few patients the side effects may require temporary reduction of the initial dosage. Generally, after five to ten days the dose may be gradually increased to the optimum response level, frequently without return of side effects. Maintenance dosage : When a good response is obtained (usually in four to twelve weeks) the dose can be reduced to 200 to 400 mg daily (but should not exceed 6 mg/kg per day) and can be continued as maintenance treatment. The minimum effective maintenance dose should be employed. The incidence of retinopathy has been reported to be higher when the maintenance dose is exceeded.
If objective improvement (such as reduced joint swelling or increased mobility) does not occur within six months the drug should be discontinued. If a relapse occurs after medication is withdrawn, therapy may be resumed or continued on an intermittent schedule if there are no ocular contraindications. Safe use of HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP for the treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis has not been established. Use in Combination Therapy : HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP may be used safely and effectively in combination with corticosteroids, salicylates, NSAIDS, and methotrexate and other second line therapeutic agents. Corticosteroids and salicylates can generally be decreased gradually in dosage or eliminated after the drug has been used for several weeks. When gradual reduction of steroid dosage is suggested, it may be done by reducing every four to five days, the dose of cortisone by no more than 5 to 15 mg; of methylprednisolone from 1 to 2 mg and dexamethasone from 0.25 to 0.5 mg. Treatment regimens using agents other than corticosteroids and NSAIDS are under development. No definitive dose combinations have been established.
Lupus Erythematosus :
In mild systemic and discoid cases, the antimalarials are the drugs of choice. The dosage of HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP depends on the severity of the disease and the patients response to treatment. For adults an initial dose of 400-800 mg daily is recommended. This level can be maintained for several weeks and then reduced to a maintenance dose of 200-400 mg daily.
Malaria :
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP is active against the erythrocytic forms of P.vivax and P.malariae and most strains of P.falciparum (but not the gametocytes of P.falciparum). HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP does not prevent relapses in patients with vivax or malariae malaria because it is not effective against exo-erythrocytic forms, nor will it prevent vivax or malariae infection when administered as a prophylactic. It is effective as a suppressive agent in patients with vivax or malariae malaria, in terminating acute attacks and significantly lengthening the interval between treatment and relapse. In patients with falciparum malaria it abolishes the acute attack and effects complete cure of the infection, unless due to a resistant strain of P.falciparum.
Malaria Suppression :
Adults
400 mg (310 mg base) on exactly the same day of each week.
Children
The weekly suppressive dose is 5 mg (base) per kg bodyweight but should not exceed the adult dose regardless of weight. Suppressive therapy should begin two weeks prior to exposure. Failing this, in adults an initial loading dose of 800 mg (620 mg base), or in children 10 mg base per kg, may be taken in two divided doses, six hours apart. The suppressive therapy should be continued for eight weeks after leaving the endemic area.
Treatment of the Acute Attack :
Adults
An initial dose of 800 mg followed by 400 mg in six to eight hours and 400 mg on each of two consecutive days. (Total dose of 2 gm or 1.55 gm base). A single dose of 800 mg (620 mg base) has also proved effective.
Children
The dosage is calculated on the basis of bodyweight. (Total dose of 25 mg base per kg).
First dose - 10 mg base per kg (not exceeding a single dose of 620 mg base).
Second dose - 5 mg base per kg (not exceeding 310 mg base), six hours after first dose.
Third dose - 5 mg base per kg eighteen hours after second dose.
Fourth dose - 5 mg base per kg twenty-four hours after third dose.
For radical cure of vivax and malariae malaria, concomitant therapy with an 8-aminoquinoline is necessary.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP is contraindicated in :
• patients with pre-existing maculopathy of the eye
• patients with known hypersensitivity to 4-aminoquinoline compounds, and
• long-term therapy in children
• children under 6 years of age.
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS :
General :
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP is not effective against chloroquine-resistant strains of P. falciparum. Children are especially sensitive to the 4-aminoquinoline compounds. A number of fatalities have been reported following the accidental ingestion of chloroquine, sometimes in relatively small doses (0.75 gm or 1 gm in one 3-year old child). Patients should be strongly warned to keep these drugs out of the reach of children. Use of hydroxychloroquine sulfate in patients with psoriasis may precipitate a severe attack of psoriasis. When used in patients with porphyria the condition may be exacerbated. The preparation should not be used in these conditions unless in the judgment of the physician the benefit to the patient outweighs the possible hazard.
PRECAUTIONS :
General :
Antimalarial compounds should be used with caution in patients with hepatic disease or alcoholism or in conjunction with known hepatotoxic drugs. Periodic blood cell counts should be made if patients are given prolonged therapy. If any severe blood disorder appears which is not attributable to the disease under treatment, discontinuation of the drug should be considered. The drug should be administered with caution in patients having G-6-PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase) deficiency.
Opthalmological :
Irreversible retinal damage has been observed in some patients who had received long-term or high-dosage 4-aminoquinolone therapy for discoid and systemic lupus erythematosus, or rheumatoid arthritis. Retinopathy has been reported to be dose related. If there is any indication of abnormality in the visual field, or retinal macular areas (such as pigmentary changes, loss of foveal reflex), or any visual symptoms (such as light flashes and streaks) which are not fully explainable by difficulties of accommodation or corneal opacities, the
drug should be discontinued immediately and the patient closely observed for possible progression. Retinal changes (and visual disturbances) may progress after cessation of therapy. All patients being treated with hydroxychloroquine should have an initial ophthalmological examination. Ophthalmological testing should be conducted at 6-monthly intervals in patients receiving hydroxychloroquine at a dose of not more than 6 mg per kg body weight per day. Ophthalmological testing should be conducted at 3-4 monthly
intervals in the following circumstances :
• Dose exceeds 6 mg per kg ideal (lean) body weight per day. Absolute body weight used as a guide to dosage, could result in an overdosage in the obese.
• Significant renal impairment
• Significant hepatic impairment
• Elderly
• Complaints of visual disturbances
• Duration of treatment exceeds 8 years.
The examination should include slit-lamp microscopy (for corneal opacities) and fundus and visual field studies. A complete eye examination before treatment will determine the presence of any visual abnormalities, either coincidental or due to the disease and establish a baseline for further assessment of the patients vision. Corneal changes often subside on reducing the dose or on interrupting therapy for a short period of time, but any suggestion of retinal change or restriction in the visual field is an indication for complete withdrawal of the drug. The use of sunglasses in patients exposed to strong sunlight is recommended, as this may be an amplifying factor in retinopathy. Observe caution in patients with hepatic or renal disease, in whom a reduction in dosage may be necessary, as well as in those taking medicines known to affect these organs. Also observe caution in patents with gastrointestinal, neurological, or blood disorders, in those with a sensitivity to quinine, and in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, porphyria and psoriasis.
Skin Reactions :
Pleomorphic skin eruptions (morbilliform, lichenoid, purpuric), itching, dryness and increased pigmentation sometimes appear after a few months of therapy. The rash is usually mild and transient. If a rash appears, Plaquenil should be withdrawn and only started again at a lower dose. Patients with psoriasis appear to be more susceptible to severe skin reactions than other patients.
Cardiac Conduction Defects :
Cases of QT interval prolongation, torsades de pointes and sudden cardiac death have been observed with hydroxychloroquine use. Although the majority of cases occurred in the overdose setting, an association with therapeutic use cannot be ruled out. Hydroxychloroquine should be used cautiously in patients with other risk factors for QT prolongation including advanced age, renal or hepatic disease, hypokalaemia or severe hypomagnesaemia, structural heart disease, bradycardia, an underlying genetic predisposition, or in patients using other potential QT prolonging medicines. HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : .
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP crosses the placenta. Use is not recommended during pregnancy except in the suppression or treatment of malaria or hepatic amoebiasis since malaria poses greater potential danger to the mother and foetus (i.e., abortion and death) than prophylactic administration of hydroxychloroquine. HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP, given in weekly chemoprophylactic doses, has not been shown to cause adverse effects in the foetus. However, risk-benefit must be considered since 4-aminoquinolines, given in therapeutic doses, have been shown to cause central nervous system (CNS) damage, including ototoxicity (auditory and vestibular); congenital deafness; retinal haemorrhages; and abnormal retinal pigmentation. In addition, HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP has been shown to accumulate selectively in melanin structures of foetal eyes. It may be retained in ocular tissues for up to 5 months after elimination from the blood.
Nursing Mothers :
One case report found that a very small amount of hydroxychloroquine is distributed into breast milk; chloroquine is also distributed into breast milk. Although problems in humans have not been documented, risk-benefit must be considered since infants and children are especially sensitive to the effects of 4-aminoquinolines.
Paediatrics :
Infants and children are especially sensitive to the effects of hydroxychloroquine and chloroquine. Fatalities have been reported following the ingestion of as little as 750 mg to 1 gram of chloroquine; hydroxychloroquine is assumed to be equally toxic. Long-term therapy with hydroxychloroquine is not generally recommended in children.
EFFECTS ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP has a major influence on the ability to drive and use machines. Impaired visual accommodation soon after the start of treatment has been reported and patients should be warned regarding driving or operating machinery. If the condition is not self-limiting, it will resolve on reducing the dose or stopping treatment.
INTERACTIONS :
It has been suggested that 4-aminoquinolines are pharmacologically incompatible with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Concomitant hydroxychloroquine and digoxin therapy may result in increased serum digoxin concentrations. Consequently serum digoxin concentrations should be closely monitored in patients receiving combination therapy. As hydroxychloroquine may enhance the effects of a hypoglycaemic treatment, a decrease in doses of insulin or antidiabetic drugs may be required.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Note : Side effects of HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP are usually dose-related. When HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP is used for the short-term treatment of malaria or other parasitic diseases, side effects are usually mild and reversible. However, following prolonged use and/or high-dose therapy, such as in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematosus, or polymorphous light eruption, side effects may be serious and sometimes irreversible. Irreversible retinal damage may be more likely to occur when the daily dosage equals or exceeds the equivalent of 310 mg (base), or 5 mg (base) per kg daily, of HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP.
The following side effects have been selected on the basis of their potential clinical significance (possible signs and symptoms in parentheses where appropriate) - not necessarily inclusive :
Those indicating need for medical attention.
Incidence less frequent.
Ocular toxicity specifically corneal opacities blurred vision or any other change in vision); keratopathy blurred vision or any other change in vision); retinopathy blurred vision or any other change in vision).
Note : The risk of retinopathy is reduced when the daily maintenance dose is less than 6.5 mg (5 mg base) per kg of body weight (mg/kg) and the cumulative dose is less than 200 grams, the duration of treatment is less than 10 years, and renal function is not impaired.
Incidence rare.
Aplastic anaemia fatigue); weakness); blood dyscrasias, specifically agranulocytosis sore throat and fever); emotional changes or psychosis mood or other mental changes); neuromyopathy increased muscle weakness); neutropenia sore throat and fever); ototoxicity any loss of hearing); ringing or buzzing in ears) - usually in patients with pre-existing auditory damage; seizures; thrombocytopenia unusual bleeding or bruising). Those indicating need for medical attention only if they continue or are bothersome.
Incidence more frequent.
Ciliary muscle dysfunction (difficulty in reading); gastrointestinal irritation (diarrhoea; loss of appetite; nausea; stomach cramps or pain; vomiting); headache; itching (especially in black patients) - not an indication for discontinuation of therapy in black patients.
Incidence less frequent.
Bleaching of hair or increased hair loss; blue-black discoloration of skin, fingernails, or inside of mouth; dizziness or lightheadedness; nervousness or restlessness; skin rash or itching. Those indicating possible retinal changes, visual disturbances and the need for medical attention if they occur or progress after medication is discontinued. Blurred vision or any other change in vision.
OVERDOSAGE :
After ingestion of an overdose of HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP, toxic symptoms may occur within 30 minutes. These include drowsiness, visual disturbances, cardiovascular collapse, and seizures, followed by sudden respiratory and cardiac arrest. Doses of chloroquine phosphate as small as 0.75 to 1 gm in children, and 2.25 to 3 gm in adults, may be fatal. It is assumed that hydroxychloroquine is equally toxic.
The following effects have been selected on the basis of their potential clinical significance (possible signs and symptoms in parenthesis where appropriate) - not necessarily inclusive :
Acute :
Cardiovascular toxicities, specifically conduction disturbances or hypotension; neurotoxicity, specifically drowsiness; headache; hyperexcitability; seizures; or coma; respiratory and cardiac arrest; visual disturbances (blurred vision)
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Since there is no specific antidote, treatment of HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP overdose should be symptomatic and supportive with possible utilization of the following :
To decrease absorption :
Emptying stomach with gastric lavage. Administering activated charcoal with a cathartic. The dose of activated charcoal should be 5 to 10 times the estimated dose of the drug ingested.
To enhance elimination :
Forcing diuresis and acidifying the urine, with ammonium chloride, for example, can help promote urinary excretion of 4-aminoquinolines. Adjusting the dose of the acidifying agent to maintain a urinary pH of 5.5 to 6.5. Monitoring of plasma potassium is recommended. Using with caution in patients with renal function impairment and/or metabolic acidosis.
Specific treatment :
For seizures : Treating repetitive seizures or status epilepticus with intravenous diazepam (in 2.5 to 5 mg increments) . For arrhythmias : Managing life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias or cardiac arrest appropriately, as per Advanced Cardiac Life Support guidelines.
For hypotension and circulatory shock : Administering fluids at a sufficient rate to maintain urine output. Administering intravenous pressors and/or inotropic drugs, such as norepinephrine, dopamine, isoproterenol, or dobutamine, if required. One study found that administration of a high-dose diazepam infusion improved hemodynamic function, and epinephrine decreased the myocardial depressant and vasodilatory effects of chloroquine overdose. This may also apply to a HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP overdose.
Monitoring :
Monitoring of plasma potassium is recommended.
Supportive care :
Securing and maintaining a patent airway, administering oxygen, and instituting assisted or controlled respiration as required. In severe overdoses, early mechanical ventilation has been suggested to prevent hypoxemia. Patients in whom intentional overdose is known or suspected should be referred for psychiatric consultation.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
HYDROXYCHLOROQUINE SULFATE TABLETS USP contains Hydroxychloroquine Sulfate USP 200 mg.
10 Blisters of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular