25 mg, 50 mg, 100 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
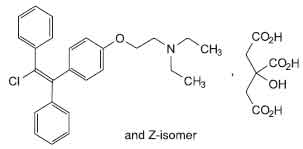
Clomifene Tablets (Clomifene Citrate) is an orally administered, non-steroidal, ovulatory stimulant which is a chemical analog of other triarylethylene compounds, such as chlorotrianisene and the cholesterol inhibitor, triparanol. Chemically, Clomifene Citrate is a mixture of both Z (trans form) and E (cis form) isomer of 2-[4-(2-chloro-1, 2-diphenylethenyl)phenoxy]-N,N-diethylethanamine dihydrogen citrate. The Z-isomer is active. The molecular formula is C26H28ClNO,C6H8O7 and molecular weight is 598.1.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
Clomifene Tablets are almost white circular, uncoated tablet having SGP embossed on one side and break line on other side.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Clomifene Citrate B.P. 50 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTIONS :
Clomifene Tablets is a drug of considerable pharmacologic potency. With careful selection and proper management of the patient, Clomifene Tablets has been demonstrated to be a useful therapy for the anovulatory patient desiring pregnancy. Clomifene Citrate is capable of interacting with oestrogen-receptor-containing tissues, including the hypothalamus, pituitary, ovary, endometrium, vagina, and cervix. It may compete with oestrogen for oestrogen-receptor-binding sites and may delay replenishment of intracellular oestrogen receptors. Clomifene Citrate initiates a series of endocrine events culminating in a preovulatory gonadotropin surge and subsequent follicular rupture. The first endocrine event in response to a course of clomifene therapy is an increase in the release of pituitary gonadotropins. This initiates steroidogenesis and folliculogenesis, resulting in growth of the ovarian follicle and an increase in the circulating level of estradiol. Following ovulation, plasma progesterone and estradiol rise and fall as they would in a normal ovulatory cycle.
Available data suggest that both the oestrogenic and antioestrogenic properties of clomifene may participate in the initiation of ovulation. Clomifene Tablets has no apparent progestational, androgenic, or antiandrogenic effects and does not appear to interfere with pituitary-adrenal or pituitary-thyroid function. Although there is no evidence of a "carryover effect" of Clomifene Tablets spontaneous ovulatory menses have been noted in some patients after Clomifene Tablets therapy.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Clomifene Tablets is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is metabolised in the liver and slowly excreted via the bile. Unchanged drug and metabolites are excreted in the faeces. The biological half-life is reported to be 5 days although traces are found in the faeces for up to 6 weeks. Enterohepatic recirculation takes place. The E-isomer is reported to be less well absorbed and more rapidly eliminated than the Z-isomer.
INDICATIONS :
Clomifene Tablets is indicated for the treatment of ovulatory failure in patients desiring pregnancy and whose husbands are fertile and potent. Impediments to this goal must be excluded or adequately treated before beginning therapy. Administration of is indicated only in patients with demonstrated ovulatory dysfunction and in whom the following conditions apply :
1. Normal liver function.
2. Physiologic indications of normal endogenous oestrogen (as estimated from vaginal smears, endometrial biopsy, assay of urinary oestrogen or from bleeding in response to progesterone). Reduced oestrogen levels, while less favorable do not prevent successful therapy.
3. Clomifene Tablets therapy is not effective for those patients with primary pituitary or ovarian failure. It cannot substitute for appropriate therapy of other disturbances leading to ovulatory dysfunction, eg. diseases of the thyroid or adrenals.
4. Particularly careful evaluation prior to Clomifene Tablets therapy should be done in patients with abnormal uterine bleeding.
It is most important that neoplastic lesions are detected. For induction of Ovulation, Amenorrhoea, Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding with anovulatory cycles. Clomifene Tablets can be used to make irregularly ovulating women to ovulate more regularly. Clomifene Tablets is useful in the treatment of Oligospermia.
Administration :
Clomifene Tablets is for oral administration.
Dosage :
General Considerations :
The workup and treatment of candidates for Clomifene Tablets therapy should be supervised by physicians experienced in management of gynaecologic or endocrine disorders. Patients should be chosen for therapy with Clomifene Tablets only after careful diagnostic evaluation. The plan of therapy should be outlined in advance. Impediments to achieving the goal of therapy must be excluded or adequately treated before beginning Clomifene Tablets The therapeutic objective should be balanced with potential risks and discussed with the patient and others involved in the achievement of a pregnancy. Ovulation most often occurs from 5 to 10 days after a course of Clomifene Tablets Coitus should be timed to coincide with the expected time of ovulation. Appropriate tests to determine ovulation may be useful during this time.
Recommended Dosage :
Treatment of the selected patient should begin with a low dose, 50 mg daily (1 tablet) for 5 days. The dose should be increased only in those patients who do not ovulate in response to cyclic 50 mg Clomifene Tablets A low dosage or duration of treatment course is particularly recommended if unusual sensitivity to pituitary gonadotropin is suspected, such as in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. The patient should be evaluated carefully to exclude pregnancy, ovarian enlargement, or ovarian cyst formation between each treatment cycle. If progestin-induced bleeding is planned, or if spontaneous uterine bleeding occurs prior to therapy, the regimen of 50 mg daily for 5 days should be started on or about the 5th day of the cycle. Therapy may be started at any time in the patient who has had no recent uterine bleeding. When ovulation occurs at this dosage, there is no advantage to increasing the dose in subsequent cycles of treatment.
If ovulation does not appear to occur after the first course of therapy, a second course of 100 mg daily (two 50 mg tablets given as a single daily dose) for 5 days should be given. This course may be started as early as 30 days after the previous one after precautions are taken to exclude the presence of pregnancy. Increasing the dosage or duration of therapy beyond 100 mg/day for 5 days is not recommended. The majority of patients who are going to ovulate will do so after the first course of therapy. If ovulation does not occur after three courses of therapy, further treatment with Clomifene Tablets is not recommended and the patient should be reevaluated. If three ovulatory responses occur, but pregnancy has not been achieved, further treatment is not recommended. If menses does not occur after an ovulatory response, the patient should be reevaluated. Long-term cyclic therapy is not recommended beyond a total of about six cycles.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Hypersensitivity :
Clomifene Tablets is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity or allergy to clomifene citrate or to any of its ingredients.
Pregnancy :
Pregnancy category X :
Although no direct effect of Clomifene citrate therapy on the human foetus has been seen established, Clomifene Tablets should not be administered in cases of suspected pregnancy as such effects have been reported in animals. To prevent inadvertent Clomifene citrate administration during early pregnancy, the basal body temperature should be recorded throughout all treatment cycles and therapy should be discontinued if pregnancy is suspected. If the basal body temperature following Clomifene citrate is biphasic and is not followed by menses, the possibility of an ovarian cyst and/or pregnancy should be excluded. Until the correct diagnosis has been determined, the next course of therapy should be delayed.
Clomifene Tablets is also contraindicated in patients who have :
1. Uncontrolled thyroid or adrenal dysfunction.
2. An organic intracranial lesion such as a pituitary tumour.
3. Liver disease or a history of liver dysfunction.
4. Abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin.
5. Ovarian cysts or enlargement not due to polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Clomifene Tablets contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS :
Visual Symptoms :
Patients should be advised that blurring or other visual symptoms such as spots or flashes (scintillating scotomata) may occasionally occur during therapy with Clomifene Tablets These visual symptoms increase in incidence with increasing total dose or therapy duration and generally disappear within a few days or weeks after Clomifene Tablets is discontinued. Patients should be warned that these visual symptoms may render such activities as driving a car or operating machinery more hazardous than usual, particularly under conditions of variable lighting. While the etiology of these visual symptoms is not yet understood, patients with any visual symptoms should discontinue treatment and have a complete ophthalmological evaluation carried out promptly.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome :
The ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) has been reported to occur in patients receiving clomifene citrate therapy for ovulation induction. In some cases, OHSS occurred following cyclic use of clomifene citrate therapy or when clomifene citrate was used in combination with gonadotropins. Transient liver function test abnormalities suggestive of hepatic dysfunction, which may be accompanied by morphologic changes on liver biopsy, have been reported in association with ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). OHSS is a medical event distinct from uncomplicated ovarian enlargement. The clinical signs of this syndrome in severe cases can include gross ovarian enlargement, gastrointestinal symptoms, ascites, dyspnoea, oliguria, and pleural effusion. In addition, the following symptoms have been reported in association with this syndrome : pericardial effusion, anasarca, hydrothorax, acute abdomen, hypotension, renal failure, pulmonary oedema, intraperitoneal and ovarian haemorrhage, deep venous thrombosis, torsion of the ovary, and acute respiratory distress. The early warning signs of OHSS are abdominal pain and distention, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and weight gain. Elevated urinary steroid levels, varying degrees of electrolyte imbalance, hypovolaemia, haemoconcentration, and hypoproteinaemia may occur. Death due to hypovolaemic shock, haemoconcentration, or thromboembolism has occurred. Due to fragility of enlarged ovaries in severe cases, abdominal and pelvic examination should be performed very cautiously. If conception results, rapid progression to the severe form of the syndrome may occur.
To minimize the hazard associated with occasional abnormal ovarian enlargement associated with Clomifene Tablets therapy, the lowest dose consistent with expected clinical results should be used. Maximal enlargement of the ovary, whether physiologic or abnormal,
may not occur until several days after discontinuation of the recommended dose of Clomifene Tablets Some patients with polycystic ovary syndrome who are unusually sensitive to gonadotropin may have an exaggerated response to usual doses of Clomifene Tablets Therefore, patients with polycystic ovary syndrome should be started on the lowest recommended dose and shortest treatment duration for the first course of therapy. If enlargement of the ovary occurs, additional Clomifene Tablets therapy should not be given until the ovaries have returned to pretreatment size, and the dosage or duration of the next course should be reduced. Ovarian enlargement and cyst formation associated with Clomifene Tablets therapy usually regresses spontaneously within a few days or weeks after discontinuing treatment. The potential benefit of subsequent Clomifene Tablets therapy in these cases should exceed the risk. Unless surgical indication for laparotomy exists, such cystic enlargement should always be managed conservatively.
A causal relationship between ovarian hyperstimulation and ovarian cancer has not been determined. However, because a correlation between ovarian cancer and nulliparity, infertility, and age has been suggested, if ovarian cysts do not regress spontaneously, a thorough evaluation should be performed to rule out the presence of ovarian neoplasia.
PRECAUTIONS :
Diagnosis Prior to Clomifene Tablets Therapy :
Careful evaluation should be given to candidates for Clomifene Tablets therapy. A complete pelvic examination should be performed prior to treatment and repeated before each subsequent course. Clomifene Tablets should not be given to patients with an ovarian cyst, as further ovarian enlargement may result. Since the incidence of endometrial carcinoma and of ovulatory disorders increases with age, endometrial biopsy should always be performed prior to Clomifene Tablets therapy in this population. If abnormal uterine bleeding is present, full diagnostic measures are necessary.
Multiple Pregnancies :
In the reviewed publications, the incidence of multiple pregnancies was increased during those cycles in which Clomifene citrate was given. The patient and her husband should be advised of the frequency and potential hazards of multiple pregnancies before starting treatment.
Additional Precaution :
Prolonged use of Clomifene Tablets may increase the risk of a borderline or invasive ovarian tumor. Clomifene Tablets should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : Pregnancy category X
Use of Clomifene Tablets in pregnancy is contraindicated.
Nursing Mothers :
It is not known whether Clomifene Tablets is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised if Clomifene Tablets is administered to a nursing woman. In some patients, Clomifene Tablets may reduce lactation.
DRUG INTERACTIONS :
Drug interactions with Clomifene Tablets have not been documented.
SIDE EFFECTS :
At the recommended dosage of Clomifene Tablets side effects occur infrequently and generally do not interfere with treatment. Adverse reactions tend to occur more frequently at higher doses and in the longer treatment courses used in some early studies. The most frequent adverse reactions to Clomifene Tablets include ovarian enlargement (approximately 1 in 7 patients), vasomotor flushes resembling menopausal symptoms, which are not usually severe and promptly disappear after treatment is discontinued (approximately 1 in
10 patients), and abdominal discomfort (approximately 1 in 15 patients). Adverse reactions which occur less frequently (approximately 1 in 50 patients or more) include breast tenderness, nausea and vomiting, nervousness, insomnia, and visual disturbances. Other side effects which occur in less than 1 in 100 patients include headache, dizziness and light-headedness, increased urination, depression, fatigue, urticaria and allergic dermatitis, abnormal uterine bleeding, weight gain, ovarian cysts (ovarian enlargement or cysts could, as such, be complicated by adnexal torsion), and reversible hair loss.
Thromboembolic events, such as pulmonary embolism, arterial occlusion, and phlebitis, have been reported rarely in patients treated with Clomifene Tablets. When Clomifene Tablets is administered at the recommended dose, abnormal ovarian enlargement is infrequent, although the usual cyclic variation in ovarian size may be exaggerated. Similarly, mid-cycle ovarian pain (mittelschmerz) may be accentuated. With prolonged or higher dosage, ovarian enlargement and cyst formation (usually luteal) may occur more often, and the luteal phase of the cycle may be prolonged. Patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome may be unusually sensitive to Clomifene Tablets therapy. Rare occurrences of massive ovarian enlargement have been reported, for example, in a patient with polyscystic ovarian syndrome whose Clomifene Tablets therapy consisted of 100 mg daily for 14 days. Since abnormal ovarian enlargement usually regresses spontaneously, most of these patients should be treated conservatively. The Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome has been reported to occur in rare cases in patients receiving Clomifene Tablets therapy. The incidence of visual symptoms, usually described as "blurring" or spots or flashes, correlates with increasing total dose. Other visual symptoms which may occur include diplopia, phosphenes, photophobia, decreased visual acuity, loss of peripheral vision, and spatial distortion. The symptoms disappear usually within a few days or weeks after Clomifene Tablets is discontinued. This may be due to intensification and/or prolongation of after-images. Symptoms often appear first, or are accentuated, upon exposure to a more brightly lit environment.
Other Laboratory Studies :
Clomifene Tablets has not been reported to cause a significant abnormality in haematologic or renal tests, in protein bound iodine, or in serum cholesterol levels.
Birth Defects :
The following medical events have been reported subsequent to pregnancies following ovulation induction therapy with Clomifene citrate : ectopic pregnancy and congenital abnormalities such as syndactyly, polydactyly, congenital heart defects, retinal aplasia, hypospadias, ovarian dysplasia, cleft lip/palate, microencephaly and neural tube defects, including anencephaly. Some medical literature reports have implied an increased occurrence of neural tube defects, while others indicate that an increased incidence over that found in the general population does not exist. Six cases of Downs syndrome, one neonatal death with multiple malformations, and one case of each of the following were reported :
club-foot, tibial torsion, blocked tear duct, and haemangioma. The other congenital abnormalities were not described. Ovarian cancer has been reported in a very small number of infertile women who have been treated with Clomifene citrate. A causal relationship between treatment with Clomifene citrate and ovarian cancer has not been established.
OVERDOSAGE AND TREATMENT OF OVERDOSE :
Signs and Symptoms :
Toxic effects accompanying acute overdosage of Clomifene Tablets have not been reported. Signs and symptoms of overdosage as a result of the use of more than the recommended dose during Clomifene Tablets therapy include nausea, vomiting, vasomotor flushes, visual blurring, spots or flashes, scotomata, ovarian enlargement with pelvic or abdominal pain.
Treatment :
In the event of overdose, appropriate supportive measures should be employed in addition to gastrointestinal decontamination.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C, protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
Clomifene Tablets contains Clomifene Citrate B.P. 50 mg.
Box of 1 strip of 10 Tablets.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular