1000 mg/5 ml
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
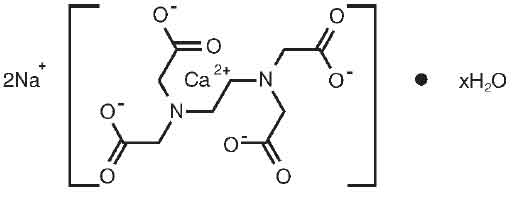
Edetate Calcium Disodium is chelating agent indicated for lead poisoning. Chemically, Edetate Calcium Disodium is Disodium [(ethylenedinitrilo)tetraacetato] calciate(2-) hydrate. The molecular formula is C10H12CaN2Na2O8.xH2O and the molecular weight is 374.27.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
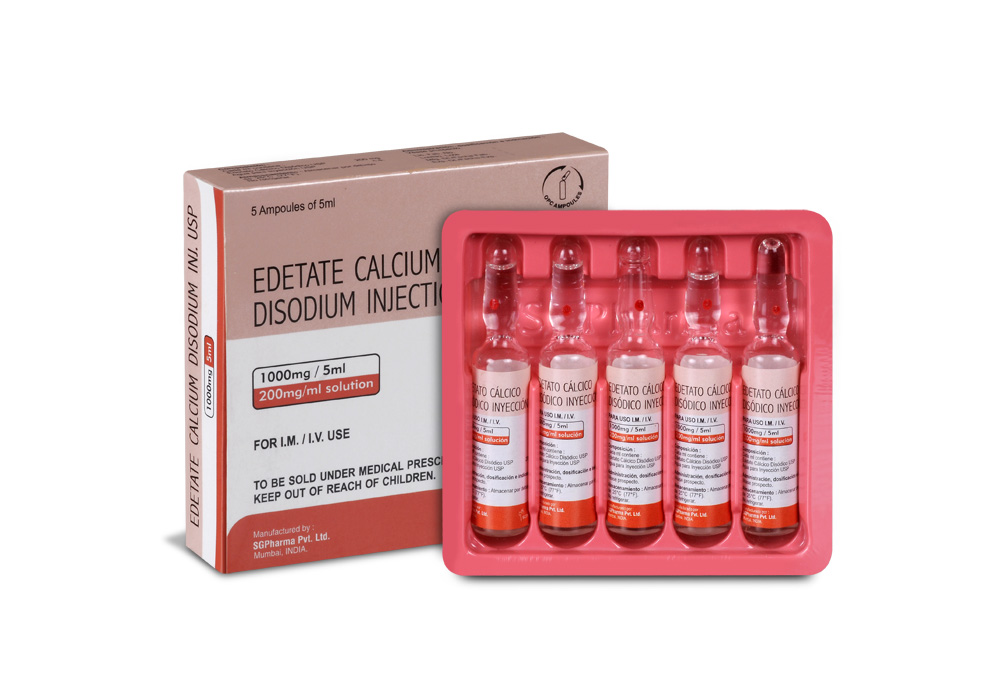
Edetate Calcium Disodium Injection USP is a sterile, clear, colourless solution filled in 5 ml ampoule.
COMPOSITION :
Each ml contains :
Edetate Calcium Disodium USP 200 mg
Water for Injection USP q.s.
Contains no preservatives.
ACTIONS :
The calcium in Edetate Calcium Disodium is readily displaced by heavy metals, such as lead, to form stable complexes. Following parenteral injection, the chelate formed is excreted in the urine, with 50 % appearing in the first hour after administration.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Edetate Calcium Disodium is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. In blood, all the drug is found in the plasma. Edetate Calcium Disodium does not appear to penetrate cells; it is distributed primarily in the extra cellular fluid with only about 5 % of the plasma concentration found in the spinal fluid. The half life of Edetate Calcium Disodium is 20 to 60 minutes. It is excreted primarily by the kidney, with about 50 % excreted in one hour and over 95 % within 24 hours. Almost none of the compound is metabolized. The primary source of lead chelated by Edetate Calcium Disodium is from bone; subsequently, soft-tissue lead is redistributed to bone when chelation is stopped. There is also some reduction in kidney lead levels following chelation therapy. It has been shown in animals that following a single dose of Edetate Calcium Disodium urinary lead output increases, blood lead concentration decreases, but brain lead is significantly increased due to internal redistribution of lead. These data are in agreement with the recent results of others in experimental animals showing that after a five day course of treatment there is no net reduction in brain lead.
INDICATIONS :
Reduction of blood levels and depot stores of lead in lead poisoning (acute and chronic) and lead encephalopathy. Chelation therapy should not replace effective measures to eliminate or reduce further exposure to lead. It may be of value in chelation of radioactive and nuclear fission products such as plutonium and yttrium. It may be worthy of trial in the treatment of poisoning from other heavy metals having a greater affinity for the chelating agent than does calcium.
Administration :
Edetate Calcium Disodium is equally effective whether administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The intramuscular route is used for all patients with overt lead encephalopathy and this route is preferred by some for young paediatric patients.
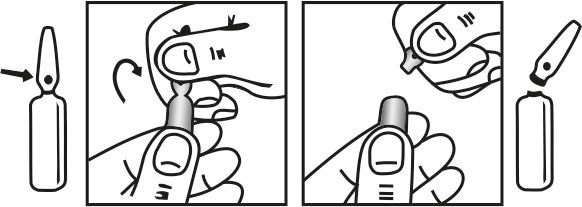
INSTRUCTION FOR USE OF AMPOULE :
The ampoule used in this product is equipped with O.P.C (One Point Cut) opening system. No ampoule file is needed to open the ampoule. The neck of the ampoule is prescored at the point of constriction. A coloured dot on the ampoule head helps to orientate the ampoule. Take the ampoule and face the coloured dot. Let the solution at the head of the ampoule to flow down by shaking or a gentle stroke. The ampoule opens easily by placing the thumb on the coloured dot and gently pressing downwards as shown.
Dosage :
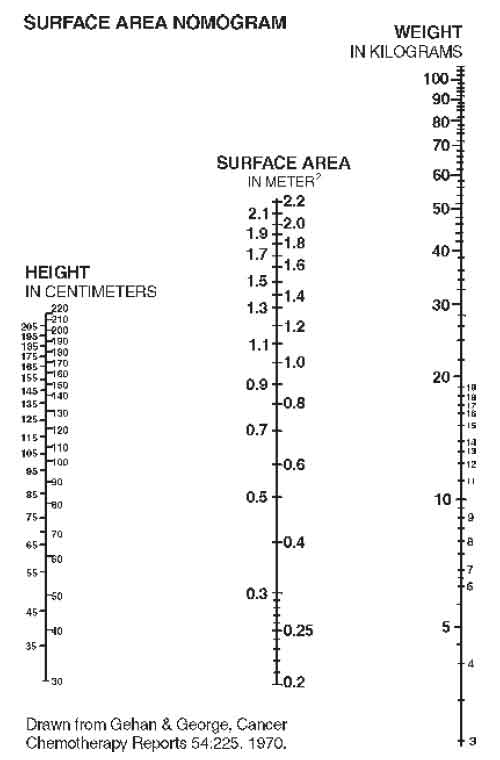
When a source for the lead intoxication has been identified, the patient should be removed from the source, if possible. The recommended dose of Edetate Calcium Disodium for asymptomatic adults and paediatric patients whose blood lead level is 70 mcg/dl but 20 mcg/dl (World Health Organization recommended upper allowable level) is 1000 mg/m2/day whether given intravenously or intramuscularly. (See Surface Area Nomogram.)
For adults with lead nephropathy, the following dosing regimen has been suggested : 500 mg/m2 every 24 hours for 5 days for patients with serum creatinine levels of 2-3 mg/dl, every 48 hours for 3 doses for patients with creatinine levels of 3-4 mg/dl, and once weekly for patients with creatinine levels above 4 mg/dl. These regimens may be repeated at one month intervals. Edetate Calcium Disodium, used alone, may aggravate symptoms in patients with very high blood lead levels. When the blood lead level is 70 mcg/dl or clinical symptoms consistent with lead poisoning are present, it is recommended that Edetate Calcium Disodium be used in conjunction with Dimercaprol. Please consult published protocols and specialized references for dosage recommendations of combination therapy.
Therapy of lead poisoning in adults and paediatric patients with Edetate Calcium Disodium is continued over a period of five days. Therapy is then interrupted for 2 to 4 days to allow redistribution of the lead and to prevent severe depletion of zinc and other essential metals. Two courses of treatment are usually employed; however, it depends on severity of the lead toxicity and the patients tolerance of the drug.
Intravenous Administration :
Add the total daily dose of Calcium Disodium (1000 mg/m2/day) to 250-500 ml of 5 % dextrose or 0.9 % sodium chloride injection. The total daily dose should be infused over a period of 8-12 hours. Edetate Calcium Disodium injection is incompatible with 10 % dextrose, 10 % invert sugar in 0.9 % sodium chloride, lactate Ringers, Ringers, one-sixth molar sodium lactate injections, and with injectable amphotericin B and hydralazine hydrochloride.
Intramuscular Administration :
The total daily dosage (1000 mg/m2/day) should be divided into equal doses spaced 8-12 hours apart. Lidocaine or procaine should be added to the Edetate Calcium Disodium injection USP to minimize pain at the injection site. The final lidocaine or procaine concentration of 5 mg/ml can be obtained as follows : 0.25 ml of 10 % lidocaine solution per 5 ml (entire content of ampoule) concentrated Edetate Calcium Disodium Injection USP 1 ml of 1 % lidocaine or procaine solution per ml of concentrated Edetate Calcium Disodium Injection USP. When used alone, regardless of method of administration, Edetate Calcium Disodium should not be given at doses larger than those recommended.
Diagnostic Test :
Several methods have been described for lead mobilization tests using Edetate Calcium Disodium to assess body stores. These procedures have advantages and disadvantages that should be reviewed in current references. Edetate Calcium Disodium mobilization tests should not be performed in symptomatic patients and in patients with blood lead levels above 55 mcg/dl for whom appropriate therapy is indicated.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Edetate Calcium Disodium should not be given during periods of anuria, nor to patients with active renal disease or hepatitis.
WARNINGS :
Edetate Calcium Disodium is capable of producing toxic effects which can be fatal. Lead encephalopathy is relatively rare in adults, but occurs more often in paediatric patients in whom it may be incipient and thus overlooked. The mortality rate in paediatric patients has been high. Patients with lead encephalopathy and cerebral oedema may experience a lethal increase in intracranial pressure following intravenous infusion; the intramuscular route is preferred for these patients. In cases where the intravenous route is necessary, avoid rapid infusion. The dosage schedule should be followed and at no time should the recommended daily dose be exceeded.
PRECAUTIONS :
General Precautions :
Edetate Calcium Disodium may produce the same renal damage as lead poisoning, such as proteinuria and microscopic haematuria. Treatment-induced nephrotoxicity is dose-dependent and may be reduced by assuring adequate diuresis before therapy begins. Urine flow must be monitored throughout therapy which must be stopped if anuria or severe oliguria develop. The proximal tubule hydropic degeneration usually recovers upon cessation of therapy. Edetate Calcium Disodium must be used in reduced doses in patients with pre-existing mild renal disease. Patients should be monitored for cardiac rhythm irregularities and other ECG changes during intravenous therapy.
Pregnancy :
The safe use of Edetate Calcium Disodium has not been established with respect to possible adverse effects upon fetal development. Therefore, it should not be used in women of childbearing potential and particularly during early pregnancy unless, in the judgment of the physician the potential benefits outweigh the possible hazards.
Labor and Delivery :
Edetate Calcium Disodium has no recognized use during labor and delivery, and its effects during these processes are unknown.
Nursing mothers :
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Edetate Calcium Disodium is administered to a nursing woman.
Paediatric Use :
Since lead poisoning occurs in paediatric populations and adults but is frequently more severe in paediatric patients. Edetate Calcium Disodium is used in patients of all ages. The intramuscular route is preferred by some for young paediatric patients. In cases where the intravenous route is necessary, avoid rapid infusion. Urine flow must be monitored throughout therapy; Edetate Calcium Disodium therapy must be stopped if anuria or severe oliguria develops. At no time should the recommended daily dosage be exceeded.
Laboratory tests :
Urinalysis and urine sediment, renal and hepatic function and serum electrolyte levels should be checked before each course of therapy and then be monitored daily during therapy in severe cases, and in less serious cases after the second and fifth day of therapy. Therapy must be discontinued at the first sign of renal toxicity. The presence of large renal epithelial cells or increasing number of red blood cells in urinary sediment or greater proteinuria call for immediate stopping of Edetate Calcium Disodium administration. Alkaline phosphatase values are frequently depressed (possibly due to decreased serum zinc levels), but return to normal within 48 hours after cessation of therapy. Elevated erythrocyte protoporphyrin levels (85 mcg/dl of whole blood) indicate the need to perform a venous blood lead determination. If the whole blood lead concentration is between 25-55 mcg/dl a mobilization test can be considered. An elevation of urinary coproporphyrin (adults : 250 mcg/day; paediatric patients under 80 lbs : 75 mcg/day) and elevation of urinary delta aminolevulinic acid (ALA) (adults : 4mg/day : paediatric patients; 3 mg/m2/day) are associated with blood lead levels 40 mcg/dl. Urinary coproporphyrin may be falsely negative in terminal patients and in severely iron-depleted paediatric patients who are not regenerating heme. In growing paediatric patients long bone x-rays showing lead lines and abdominal x-rays showing radio-opaque material in the abdomen may be of help in estimating the level of exposure to lead.
INTERACTIONS :
There is no known drug interference with standard clinical laboratory tests. Steroids enhance the renal toxicity of Edetate Calcium Disodium in animals. Edetate Calcium Disodium interferes with the action of zinc insulin preparations by chelating the zinc.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The following adverse effects have been associated with the use of Edetate Calcium Disodium :
Body as a Whole : pain at intramuscular injection site, fever, chills, malaise, fatigue, myalgia, arthralgia.
Cardiovascular : hypotension, cardiac rhythm irregularities.
Renal : acute necrosis of proximal tubules (which may result in fatal nephrosis). Infrequent changes in distal tubules and glomeruli.
Urinary : glycosuria, proteinuria, microscopic haematuria and large epithelial cells in urinary sediment.
Nervous System : tremors, headache, numbness, tingling.
Gastrointestinal : cheilosis, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, excessive thirst.
Hepatic : mild increases in SGOT and SGPT are common, and return to normal within 48 hours after cessation of therapy.
Immunogenic : histamine-like reactions (sneezing, nasal congestion, Iacrimation), rash.
Hematopoietic : transient bone marrow depression, anaemia.
Metabolic : zinc deficiency, hypercalcaemia.
OVERDOSAGE :
Symptoms :
Inadvertent administration of 5 times the recommended dose, infused intravenously over a 24 hour period, to an asymptomatic 16 month old patient with a blood lead content of 56 mcg/dl did not cause any ill effects. Edetate Calcium Disodium can aggravate the symptoms of severe lead poisoning therefore, most toxic effects (cerebral oedema, renal tubular necrosis) appear to be associated with lead poisoning. Because of cerebral oedema, a therapeutic dose may be lethal to an adult or a paediatric patient with lead encephalopathy. Higher dosage of Edetate Calcium Disodium may produce a more severe zinc deficiency.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Cerebral oedema should be treated with repeated doses of mannitol. Steroids enhance the renal toxicity of Edetate Calcium Disodium in animals and, therefore are no longer recommended. Zinc levels must be monitored. Good urinary output must be maintained because diuresis will enhance drug elimination. It is not known if Edetate Calcium Disodium is dialyzable.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F).
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
Edetate Calcium Disodium Injection USP is supplied as 1000 mg of Edetate Calcium Disodium in 5 ml Ampoule.
Such 5 ampoules of 5 ml are packed in a Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular