100 mg, 125 mg, 250 mg,
400 mg, 500 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
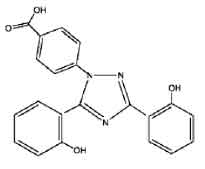
DEFERASIROX TABLETS is an iron chelating agent. Chemically, Deferasirox is 4-[3,5-Bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]-benzoic acid. The molecular formula is C21H15N3O4 and molecular weight is 373.4
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
DEFERASIROX TABLETS are white to off white circular, flat, uncoated tablet with breakline on one side.
COMPOSITION :
Each tablet for oral suspension contains :
Deferasirox 100 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTION :
Deferasirox is an orally active chelator that is selective for iron (as Fe3+). It is a tridentate ligand that binds iron with high affinity in a 2:1 ratio. Although deferasirox has very low affinity for zinc and copper there are variable decreases in the serum concentration of these trace metals after the administration of deferasirox. The clinical significance of these decreases is uncertain.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Absorption :
Deferasirox is absorbed following oral administration with median times to maximum plasma concentration (tmax) of about 1.5 to 4 hours. The Cmax and AUC of deferasirox increase approximately linearly with dose after both single administration and under steady-state conditions. Exposure to deferasirox increased by an accumulation factor of 1.3 to 2.3 after multiple doses. The absolute bioavailability (AUC) of deferasirox tablets for oral suspension is 70 % compared to an intravenous dose. The bioavailability (AUC) of deferasirox
was variably increased when taken with a meal.
Distribution :
Deferasirox is highly (~99 %) protein bound almost exclusively to serum albumin. The percentage of deferasirox confined to the blood cells was 5 % in humans. The volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) of deferasirox is 14.37 ± 2.69 L in adults.
Metabolism :
Glucuronidation is the main metabolic pathway for deferasirox, with subsequent biliary excretion. Deconjugation of glucuronidates in the intestine and subsequent reabsorption (enterohepatic recycling) is likely to occur. Deferasirox is mainly glucuronidated by UGT1A1 and to a lesser extent UGT1A3. CYP450-catalyzed (oxidative) metabolism of deferasirox appears to be minor in humans (about 8 %). Deconjugation of glucuronide metabolites in the intestine and subsequent reabsorption (enterohepatic recycling) was confirmed in a
healthy volunteer study in which the administration of cholestyramine 12 gm twice daily (strongly binds to deferasirox and its conjugates) 4 and 10 hours after a single dose of deferasirox resulted in a 45 % decrease in deferasirox exposure (AUC) by interfering with the enterohepatic recycling of deferasirox.
Excretion :
Deferasirox and metabolites are primarily (84 % of the dose) excreted in the faeces. Renal excretion of deferasirox and metabolites is minimal (8 % of the administered dose). The mean elimination half-life (t1/2) ranged from 8-16 hours following oral administration.
INDICATIONS :
DEFERASIROX TABLETS is indicated for the treatment of chronic iron overload due to frequent blood transfusions (≥7 ml/kg/month of packed red blood cells) in patients with beta thalassaemia major aged 6 years and older. DEFERASIROX TABLETS is also indicated for the treatment of chronic iron overload due to blood transfusions when deferoxamine therapy is contraindicated or inadequate in the following patient groups :
• In patients with beta thalassaemia major with iron overload due to frequent blood transfusions (≥7 ml/kg/month of packed red blood cells) aged 2 to 5 years,
• In patients with beta thalassaemia major with iron overload due to infrequent blood transfusions (<7 ml/kg/month of packed red blood cells) aged 2 years and older,
• In patients with other anaemias aged 2 years and older.
Administration :
DEFERASIROX TABLETS are for oral suspension.
Method of administration :
DEFERASIROX TABLETS must be taken once daily on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before food, preferably at the same time each day. The tablets are dispersed by stirring in a glass of water or orange or apple juice (100 to 200 ml) until a fine suspension is obtained. After the suspension has been swallowed, any residue must be resuspended in a small volume of water or juice and swallowed. The tablets must not be chewed or swallowed whole.
Dosage :
Adult and child over 2 years initially 10-30 mg/kg once daily according to serum- ferritin concentration and amount of transfused blood; maintenance, adjust dose every 3-6 months in steps of 5-10 mg/kg according to serum-ferritin concentration; max. 30 mg/kg daily.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Creatinine clearance <40 ml/min or serum creatinine >2 times the age-appropriate upper limit of normal. Platelet counts < 50 x 109/l. High risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) patients and patients with other haematological and non-haematological malignancies who are not expected to benefit from chelation therapy due to the rapid progression of their disease. Hypersensitivity to the active substance or to any of the excipients.
WARNINGS :
Cytopenias :
There have been postmarketing reports (both spontaneous and from clinical trials) of cytopenias, including agranulocytosis, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, in patients treated with DEFERASIROX TABLETS. Some of these patients died. The relationship of these episodes to treatment with DEFERASIROX TABLETS is uncertain. Most of these patients had preexisting haematologic disorders that are frequently associated with bone marrow failure. In line with the standard clinical management of such haematological disorders,
blood counts should be monitored regularly. Interruption of treatment with DEFERASIROX TABLETS should be considered in patients who develop unexplained cytopenia. Reintroduction of therapy with DEFERASIROX TABLETS may be considered, once the cause of the cytopenia has been elucidated.
Hypersensitivity :|
Serious hypersensitivity reactions (such as anaphylaxis and angiooedema) have been reported in patients receiving DEFERASIROX TABLETS, with the onset of the reaction occurring in the majority of cases within the first month of treatment. If reactions are severe, DEFERASIROX TABLETS should be discontinued and appropriate medical intervention instituted.
Special Senses :
Auditory disturbances (high frequency hearing loss, decreased hearing), and ocular disturbances (lens opacities, cataracts, elevations in intraocular pressure, and retinal disorders) have been reported at a frequency of <1 % with DEFERASIROX TABLETS therapy in the clinical studies. Auditory and ophthalmic testing (including slit lamp examinations and dilated fundoscopy) are recommended before starting DEFERASIROX TABLETS treatment and thereafter at regular intervals (every 12 months). If disturbances are noted, dose reduction or interruption should be considered.
PRECAUTIONS :
General :
Skin rashes may occur during DEFERASIROX TABLETS treatment. For rashes of mild to moderate severity, DEFERASIROX TABLETS may be continued without dose adjustment, since the rash often resolves spontaneously. In severe cases, DEFERASIROX TABLETS may be interrupted. Reintroduction at a lower dose with escalation may be considered in combination with a short period of oral steroid administration.
Laboratory Tests :
Serum ferritin should be measured monthly to assess response to therapy and to evaluate for the possibility of overchelation of iron. If the serum ferritin falls consistently below 500 mcg/l, consideration should be given to temporarily interrupting therapy with
DEFERASIROX TABLETS. In the clinical studies, the correlation coefficient between the serum ferritin and LIC was 0.63. Therefore, changes in serum ferritin levels may not always reliably reflect changes in LIC. Laboratory monitoring of renal and hepatic function should be performed.
Pregnancy : Category C
Deferasirox was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits treated with doses up to and exceeding the maximum tolerated doses. Foetal developmental impairment and increased skeletal variations were seen in rats at a maternotoxic dose of 100 mg/kg/day which achieved a drug exposure (plasma AUC) that was similar to the maximum human value. No adverse effects on foetal development was observed in rabbits at a maternotoxic dose of 50 mg/kg/day which achieved a drug exposure about 30 % of the maximum human value. Treatment of rats with a maternotoxic dose of 90 mg/kg/day from early gestation to end of lactation resulted in increased stillborn pups and reduced pup birthweight. No effect was seen with 30 mg/kg/day which achieved a drug exposure about 20 % of the maximum human value.
Adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women have not been conducted. Deferasirox should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the foetus.
Nursing Mothers :
It is not known if deferasirox is secreted into human milk. In an animal study, deferasirox was present in the milk of rats at higher concentration than in maternal plasma. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, women should be advised against breast-feeding while taking deferasirox.
EFFECT ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
No studies on the effects of DEFERASIROX TABLETS on the ability to drive or use machines have been performed. Patients experiencing the uncommon adverse effect of dizziness should exercise caution when driving or operating machinery.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
The safety of DEFERASIROX TABLETS in combination with other iron chelators has not been established. Therefore, it must not be combined with other iron chelator therapies. The concomitant administration of DEFERASIROX TABLETS with substances that have known ulcerogenic potential, such as NSAIDs (including acetylsalicylic acid at high dosage), corticosteroids or oral bisphosphonates may increase the risk of gastrointestinal toxicity. The concomitant administration of DEFERASIROX TABLETS with anticoagulants may also increase the risk of gastrointestinal haemorrhage. Close clinical monitoring is required when deferasirox is combined with these substances. The bioavailability of deferasirox was increased to a variable extent when taken along with food. DEFERASIROX TABLETS must therefore be taken on an empty stomach at least 30 minutes before food, preferably at the same time each day. Deferasirox metabolism depends on UGT enzymes. In a healthy volunteer study, the concomitant administration of DEFERASIROX TABLETS (single
dose of 30 mg/kg) and the potent UGT inducer, rifampicin, (repeated dose of 600 mg/day) resulted in a decrease of deferasirox exposure by 44 % (90 % CI : 37 % - 51 %). Therefore, the concomitant use of DEFERASIROX TABLETS with potent UGT inducers (e.g. rifampicin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital, ritonavir) may result in a decrease in DEFERASIROX TABLETS efficacy. The patient’s serum ferritin should be monitored during and after the combination, and the dose of DEFERASIROX TABLETS adjusted if necessary.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Gastro-intestinal disturbances (including ulceration and haemorrhage); headache; proteinuria; pruritus, rash; less commonly hepatitis, cholelithiasis, oedema, fatigue, anxiety, sleep disorder, dizziness, pyrexia, pharyngitis, glucosuria, renal tubulopathy, disturbances of hearing and vision (including lens opacity and maculopathy), and skin pigmentation; hepatic failure, acute renal failure, blood disorders (including agranulocytosis, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia), hypersensitivity reactions (including anaphylaxis and angioedema) also reported.
OVERDOSAGE :
Cases of overdose (2-3 times the prescribed dose for several weeks) have been reported. In one case, this resulted in hepatitis which resolved without long-term consequences after a dose interruption. Single doses up to 80 mg/kg/day in iron overloaded â-thalassemic patients have been tolerated with nausea and diarrhoea noted. In healthy volunteers, single doses of up to 40 mg/kg/day were tolerated. Acute signs of overdose may include nausea, vomiting, headache & diarrhoea.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
There is no specific antidote for DEFERASIROX TABLETS. In case of overdose, induce vomiting and gastric lavage. Also give symptomatic treatment as needed.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
DEFERASIROX TABLETS contains Deferasirox 100 mg.
3 strips of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular