100 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
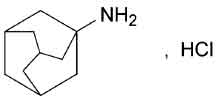
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS (Amantadine Hydrochloride) is a weak dopamine agonist with modest antiparkinsonian effects. Chemically, Amantadine Hydrochloride is Tricyclo[3.3.1.13,7] decan-1amine hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C10H17N,HCl and molecular weight is 187.7
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are orange coloured, circular biconvex uncoated tablets with breakline on one side.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Amantadine Hydrochloride B.P. 100 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Aluminium Lake Sunset Yellow.
ACTIONS :
Parkinson’s disease : Amantadine Hydrochloride has been shown to be a low affinity antagonist at the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) subtype of glutamate receptors. Overactivity of glutamatergic neurotransmission has been implicated in the generation of parkinsonian symptoms. The clinical efficacy of amantadine is thought to be mediated through its antagonism at the NMDA subtype of glutamate receptors. In addition, amantadine may also exert some anticholinergic activity.
Herpes Zoster :
The mechanism of action of Amantadine Hydrochloride in herpes zoster has not been fully characterised.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Amantadine Hydrochloride is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract; peak concentrations in the plasma appear within about 4 hours after oral doses. Plasma protein binding is reported to be about 67 %, with a substantial amount bound to erythrocytes; the concentration is about 2.7 times higher in erythrocytes than in plasma. It is mainly excreted unchanged in the urine by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion although small amounts of an acetylated metabolite have also been detected in urine; the plasma elimination half-life is reported to be about 15 hours in patients with normal renal function but is significantly prolonged in the elderly and in patients with renal impairment. The rate of elimination may be increased by acidification of the urine. Amantadine crosses the placenta and the blood-brain barrier. It is also distributed into breast milk.
INDICATIONS :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of signs and symptoms of infection caused by various strains of influenza A virus. AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are also indicated in the treatment of parkinsonism and drug-induced extrapyramidal reactions.
Influenza A Prophylaxis :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are indicated for chemoprophylaxis against signs and symptoms of influenza A virus infection. Because AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS do not completely prevent the host immune response to influenza A infection, individuals who take this drug may still develop immune responses to natural disease or vaccination and may be protected when later exposed to antigenically related viruses. Following vaccination during an influenza A outbreak, AMANTADINE
HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS prophylaxis should be considered for the 2- to 4- week time period required to develop an antibody response.
Influenza A Treatment :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are also indicated in the treatment of uncomplicated respiratory tract illness caused by influenza A virus strains especially when administered early in the course of illness. There are no well-controlled clinical studies demonstrating that treatment with AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS will avoid the development of influenza A virus pneumonitis or other complications in high risk patients. There is no clinical evidence indicating that AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are effective in the prophylaxis or treatment of viral respiratory tract illnesses other than those caused by influenza A virus strains.
The following points should be considered before initiating treatment or prophylaxis with AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS :
• AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are not a substitute for early vaccination on an annual basis as recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices.
• Influenza viruses change over time. Emergence of resistance mutations could decrease drug effectiveness. Other factors (for example, changes in viral virulence) might also diminish clinical benefit of antiviral drugs. Prescribers should consider available information on influenza drug susceptibility patterns and treatment effects when deciding whether to use AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS.
Parkinson’s Disease / Syndrome :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are indicated in the treatment of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease (Paralysis Agitans), postencephalitic parkinsonism, and symptomatic parkinsonism which may follow injury to the nervous system by carbon monoxide intoxication. It is indicated in those elderly patients believed to develop parkinsonism in association with cerebral arteriosclerosis. In the treatment of Parkinson’s disease, AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are less effective than levodopa, (-)-3-(3,4-
ihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine, and its efficacy in comparison with the anticholinergic antiparkinson drugs has not yet been established.
Drug-Induced Extrapyramidal Reactions :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are indicated in the treatment of drug-induced extrapyramidal reactions. Although anticholinergic-type side effects have been noted with AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS when used in patients with drug-induced extrapyramidal reactions, there is a lower incidence of these side effects than that observed with the anticholinergic antiparkinson drugs.
Administration :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is for oral administration. Administer after meals or with food. Do not administer at bedtime because drug may cause insomnia.
Dosage :
The dose of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS may need reduction in patients with congestive heart failure, peripheral oedema, orthostatic hypotension, or impaired renal function.
Dosage for Prophylaxis and Treatment of Uncomplicated Influenza A Virus Illness
Adult :
The adult daily dosage of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is 200 mg; two 100 mg tablets as a single daily dose. The daily dosage may be split into one tablet of 100 mg twice a day. If central nervous system effects develop in once-a-day dosage, a split dosage schedule may reduce such complaints. In persons 65 years of age or older, the daily dosage of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is 100 mg. A 100 mg daily dose has also been shown in experimental challenge studies to be effective as prophylaxis in healthy adults who are not at high risk for influenza-related complications. However, it has not been demonstrated that a 100 mg daily dose is as effective as a 200 mg daily dose for prophylaxis, nor has the 100 mg daily dose been studied in the treatment of acute
influenza illness. In recent clinical trials, the incidence of central nervous system (CNS) side effects associated with the 100 mg daily dose was at or near the level of placebo. The 100 mg dose is recommended for persons who have demonstrated intolerance to 200 mg of Amantadine Hydrochloride Tablets daily because of CNS or other toxicities.
Paediatric Patients :
1 yr. to 9 yrs. of age The total daily dose should be calculated on the basis of 2 to 4 mg/lb/day (4.4 to 8.8 mg/kg/day), but not to exceed 150 mg per day. 9 yrs. to 12 yrs. of age The total daily dose is 200 mg given as one tablet of 100 mg twice a day. The 100 mg daily dose has not been studied in this paediatric population. Therefore, there are no data which demonstrate that this dose is as effective as or is safer than the 200 mg daily dose in this patient population. Prophylactic dosing should be started in anticipation of an influenza A
outbreak and before or after contact with individuals with influenza A virus respiratory tract illness. AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should be continued daily for at least 10 days following a known exposure. If AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are used chemoprophylactically in conjunction with inactivated influenza A virus vaccine until protective antibody responses develop, then it should be administered for 2 to 4 weeks after the vaccine has been given. When inactivated influenza A virus vaccine is unavailable or contraindicated, AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should be administered for the duration of known influenza A in the community because of repeated and unknown exposure. Treatment of influenza A virus illness should be started as soon as possible, preferably within 24 to 48 hours after onset of signs and symptoms, and should be continued for 24 to 48 hours after the disappearance of signs and symptoms.
Dosage for Parkinsonism
Adult :
The usual dose of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is 100 mg twice a day when used alone. AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS have an onset of action usually within 48 hours. The initial dose of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is
100 mg daily for patients with serious associated medical illnesses or who are receiving high doses of other antiparkinson drugs. After one to several weeks at 100 mg once daily, the dose may be increased to 100 mg twice daily, if necessary. Occasionally, patients whose responses are not optimal with AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS at 200 mg daily may benefit from an increase up to 400 mg daily in divided doses. However, such patients should be supervised closely by their physicians. Patients initially deriving benefit from AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS not uncommonly experience a fall-off of effectiveness after a few months. Benefit may be regained by increasing the dose to 300 mg daily. Alternatively, temporary discontinuation of AMANTADINE
HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS for several weeks, followed by reinitiation of the drug, may result in regaining benefit in some patients. A decision to use other antiparkinson drugs may be necessary.
Dosage for the Concomitant Therapy
Some patients who do not respond to anticholinergic antiparkinson drugs may respond to AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS. When AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS or anticholinergic antiparkinson drugs are each used with marginal benefit, concomitant use may produce additional benefit. When AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS and levodopa are initiated concurrently, the patient can exhibit rapid therapeutic benefits. AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should be held constant at 100 mg daily or twice daily while the daily dose of levodopa is gradually increased to optimal benefit.When AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS are added to optimal well-tolerated doses of levodopa, additional benefit may result, including smoothing out the fluctuations in improvement which sometimes occur in patients on levodopa alone. Patients who require a reduction in their usual dose of levodopa because of development of side effects may possibly regain lost benefit with the addition of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS.
Dosage for Drug-Induced Extrapyramidal Reactions
Adult :
The usual dose of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is 100 mg twice a day. Occasionally, patients whose responses are not optimal with AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS at 200 mg daily may benefit from an increase up to 300 mg daily in divided doses.Dosage for Impaired Renal Function Depending upon creatinine clearance, the following dosage adjustments are recommended.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Known hypersensitivity to amantadine or any of the excipients. Individuals subject to convulsions. A history of gastric ulceration. Severe renal disease. Pregnancy.
WARNINGS :
Deaths :
Deaths have been reported from overdose with AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS. The lowest reported acute lethal dose was 1 gram. Acute toxicity may be attributable to the anticholinergic effects of amantadine. Drug overdose has resulted in cardiac, respiratory, renal or central nervous system toxicity. Cardiac dysfunction includes arrhythmia, tachycardia and hypertension. Deaths due to drug accumulation (overdosage) have been reported in patients with renal impairment, who were prescribed higher than
recommended doses of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS for their level of renal function.
Suicide Attempts :
Suicide attempts, some of which have been fatal, have been reported in patients treated with amantadine hydrochloride, many of whom received short courses for influenza treatment or prophylaxis. The incidence of suicide attempts is not known and the pathophysiologic mechanism is not understood. Suicide attempts and suicidal ideation have been reported in patients with and without prior history of psychiatric illness. Amantadine hydrochloride can exacerbate mental problems in patients with a history of psychiatric disorders or substance abuse. Patients who attempt suicide may exhibit abnormal mental states which include disorientation, confusion, depression, personality changes, agitation, aggressive behaviour, hallucinations, paranoia, other psychotic reactions, and somnolence or
insomnia. Because of the possibility of serious adverse effects, caution should be observed when prescribing AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS to patients being treated with drugs having CNS effects, or for whom the potential risks outweigh the benefit of treatment.
CNS Effects :
Patients with a history of epilepsy or other “seizures” should be observed closely for possible increased seizure activity.Patients receiving AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS who note central nervous system effects or blurring of vision should be cautioned against driving or working in situations where alertness and adequate motor coordination are important.
Other :
Patients with a history of congestive heart failure or peripheral oedema should be followed closely as there are patients who developed congestive heart failure while receiving AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS. Patients with Parkinson’s disease improving on AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should resume normal activities gradually and cautiously, consistent with other medical considerations, such as the presence of osteoporosis or phlebothrombosis. Because AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS have anticholinergic effects and may cause mydriasis, it should not be given to patients with untreated angle closure glaucoma.
EFFECT ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
AMANTADINE HYDROCLORIDE TABLETS may cause adverse reactions like drowsiness, visual disturbances, vertigo and dizziness that could affect the ability to drive or use machines.
PRECAUTIONS :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should not be discontinued abruptly in patients with Parkinson’s disease since a few patients have experienced a parkinsonian crisis, i.e., a sudden marked clinical deterioration, when this medication was suddenly stopped. The dose of anticholinergic drugs or of amantadine hydrochloride should be reduced if atropine-like effects appear when these drugs are used concurrently. Abrupt discontinuation may also precipitate delirium, agitation, delusions, hallucinations, paranoid reaction, stupor, anxiety, depression and slurred speech.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) :
Sporadic cases of possible Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) have been reported in association with dose reduction or withdrawal of amantadine hydrochloride therapy. Therefore, patients should be observed carefully when the dosage of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is reduced abruptly or discontinued, especially if the patient is receiving neuroleptics. NMS is an uncommon but life-threatening syndrome characterized by fever or hyperthermia; neurologic findings including muscle rigidity, involuntary
movements, altered consciousness; mental status changes; other disturbances such as autonomic dysfunction, tachycardia, tachypnea, hyper- or hypotension; laboratory findings such as creatine phosphokinase elevation, leukocytosis, myoglobinuria, and increased serum myoglobin. The early diagnosis of this condition is important for the appropriate management of these patients. Considering NMS as a possible diagnosis and ruling out other acute illnesses (e.g., pneumonia, systemic infection, etc.) is essential. This may be especially complex if the clinical presentation includes both serious medical illness and untreated or inadequately treated extrapyramidal signs and symptoms (EPS). Other important considerations in the differential diagnosis include central anticholinergic toxicity, heat stroke, drug fever and primary central nervous system (CNS) pathology.
The management of NMS should include :
1) intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring, and 2) treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems for which specific treatments are available. Dopamine agonists, such as bromocriptine, and muscle relaxants, such as dantrolene are often used in the treatment of NMS, however, their effectiveness has not been demonstrated in controlled studies.
Renal disease :
Because amantadine hydrochloride is mainly excreted in the urine, it accumulates in the plasma and in the body when renal function declines. Thus, the dose of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should be reduced in patients with renal impairment and in individuals who are 65 years of age or older.
Liver disease :
Care should be exercised when administering AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS to patients with liver disease. Rare instances of reversible elevation of liver enzymes have been reported in patients receiving amantadine hydrochloride, though a specific relationship between the drug and such changes has not been established.
Pregnancy : Category C
Teratogenic Effects.
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS should not be used during pregnancy; embryo toxicity and teratogenicity have been reported in rats given high doses.
Nursing mothers : Amantadine Hydrochloride is excreted in human milk. Use is not recommended in nursing mothers.
Paediatric Use : Appropriate studies on the relationship of age to the effects of amantadine have not been performed in neonates and infants up to one year of age. However, use of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS in children older than 1 year of age has not been shown to cause any paediatrics specific problems that would limit its usefulness in children.
INTERACTIONS :
Careful observation is required when AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS is administered concurrently with central nervous system stimulants. Agents with anticholinergic properties may potentiate the anticholinergic-like side effects of amantadine.
Coadministration of thioridazine has been reported to worsen the tremor in elderly patients with Parkinson’s disease, however, it is not known if other phenothiazines produce a similar response. Coadministration of Dyazide (triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide) resulted in a higher plasma amantadine concentration in a 61-year-old man receiving amantadine hydrochloride 100 mg TID. for Parkinson’s disease. It is not known which of the components of Dyazide contributed to the observation or if related drugs produce a similar response.
Coadministration of quinine or quinidine with amantadine was shown to reduce the renal clearance of amantadine by about 30 %. The concurrent use of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS with live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) intranasal has not been
evaluated. However, because of the potential for interference between these products, LAIV should not be administered within 2 weeks before or 48 hours after administration of amantadine hydrochloride, unless medically indicated. The concern about possible interference arises from the potential for antiviral drugs to inhibit replication of live vaccine virus. Trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine can be administered at any time relative to use of amantadine hydrochloride. AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS may also interact with Procainamide, Sotalol, Chlorpromazine, Haloperidol, Amitriptyline, Erythromycin, Clarythromycin, Co-trimoxazole and decrease the tolerance to Alcohol.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The side effects reported most frequently at the recommended dose of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS (5 to 10 %) are : nausea, dizziness (lightheadedness), and insomnia. Less frequently (1 to 5 %) reported side effects are : depression, anxiety and irritability, hallucinations, confusion, anorexia, dry mouth, constipation, ataxia, livedo reticularis, peripheral oedema, orthostatic hypotension, headache, somnolence, nervousness, dream abnormality, agitation, dry nose, diarrhoea and fatigue. Infrequently (0.1 to 1 %) occurring side effects are : congestive heart failure, psychosis, urinary retention, dyspnoea, skin rash, vomiting, weakness, slurred speech, euphoria, thinking abnormality, amnesia, hyperkinesia, hypertension, decreased libido, and visual disturbance, including punctate subepithelial or other corneal opacity, corneal oedema, decreased visual acuity, sensitivity to light, and optic nerve palsy.
Rare (less than 0.1 %) occurring side effects are : instances of convulsion, leukopenia, neutropenia, eczematoid dermatitis, oculogyric episodes, suicidal attempt, suicide, and suicidal ideation.
Other side effects reported during postmarketing experience with amantadine hydrochloride usage include :
Nervous System/Psychiatric : Coma, stupor, delirium, hypokinesia, hypertonia, delusions, aggressive behaviour, paranoid reaction, manic reaction, involuntary muscle contractions, gait abnormalities, paresthesia, EEG changes, and tremor. Abrupt discontinuation may also precipitate delirium, agitation, delusions, hallucinations, paranoid reaction, stupor, anxiety, depression and slurred speech.
Cardiovascular : Cardiac arrest, arrhythmias including malignant arrhythmias, hypotension and tachycardia.
Respiratory : Acute respiratory failure, pulmonary oedema, and tachypnea.
Gastrointestinal : Dysphasia.
Haematologic : Leukocytosis, agranulocytosis.
Special Senses : Keratitis and mydriasis.
Skin and Appendages : Pruritus and diaphoresis.
Miscellaneous : Neuroleptic malignant syndrome, allergic reactions including anaphylactic reactions, oedema and fever.
Laboratory Test : Elevated : CPK, BUN, serum creatinine, alkaline phosphatase, LDH, bilirubin, GGT, SGOT, and SGPT.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS :
Patients should be advised of the following information :
Blurry vision and/or impaired mental acuity may occur. Gradually increase physical activity as the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease improve. Avoid excessive alcohol usage, since it may increase the potential for CNS effects such as dizziness, confusion, lightheadedness and orthostatic hypotension. Avoid getting up suddenly from a sitting or lying position. If dizziness or lightheadedness occurs, notify physician. Notify physician if mood/mental changes, swelling of extremities, difficulty urinating and/or shortness of breath occur. Do not take more medication than prescribed because of the risk of overdose. If there is no improvement in a few days, or if medication appears less effective after a few weeks, discuss with a physician. Consult physician before discontinuing medication. Seek medical attention immediately if it is suspected that an overdose of medication has been taken.
OVERDOSAGE :
Deaths have been reported from overdose with AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS. The lowest reported acute lethal dose was 1 gram. Because some patients have attempted suicide by overdosing with amantadine, prescriptions should be written for the smallest quantity consistent with good patient management. Acute toxicity may be attributable to the anticholinergic effects of amantadine. Drug overdose has resulted in cardiac, respiratory, renal or central nervous system toxicity. Cardiac dysfunction includes arrhythmia, tachycardia and hypertension. Pulmonary oedema and respiratory distress (including adult respiratory distress syndrome - ARDS) have been reported; renal dysfunction including increased BUN, decreased creatinine clearance and renal insufficiency can occur. Central nervous system effects that have been reported include insomnia, anxiety, agitation, aggressive behaviour, hypertonia, hyperkinesia, ataxia, gait abnormality, tremor, confusion, disorientation, depersonalization, fear, delirium, hallucinations, psychotic reactions, lethargy, somnolence and coma. Seizures may be exacerbated in patients with prior history of seizure disorders. Hyperthermia has also been observed in cases where a drug overdose has occurred.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
There is no specific antidote for an overdose of AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS. However, slowly administered intravenous physostigmine in 1 and 2 mg doses in an adult at 1- to 2-hour intervals and 0.5 mg doses in a child at 5- to 10-minute intervals up to a maximum of 2 mg/hour have been reported to be effective in the control of central nervous system toxicity caused by amantadine hydrochloride. For acute overdosing, general supportive measures should be employed along with immediate gastric lavage or induction of emesis. Fluids should be forced, and if necessary, given intravenously. The pH of the urine has been reported to influence the excretion rate of amantadine hydrochloride. Since the excretion rate of amantadine hydrochloride increases rapidly when the urine is acidic, the administration of urine acidifying drugs may increase the elimination of the drug from the body. The blood pressure, pulse, respiration and temperature should be monitored. The patient should be observed for hyperactivity and convulsions; if required, sedation, and
anticonvulsant therapy should be administered. The patient should be observed for the possible development of arrhythmias and hypotension; if required, appropriate antiarrhythmic and antihypotensive therapy should be given. Electrocardiographic monitoring may be required after ingestion, since malignant tachyarrhythmias can appear after overdose.
Care should be exercised when administering adrenergic agents, such as isoproterenol, to patients with an amantadine hydrochloride overdose, since the dopaminergic activity of amantadine hydrochloride has been reported to induce malignant arrhythmias. The blood electrolytes, urine pH and urinary output should be monitored. If there is no record of recent voiding, catheterization should be done.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C, protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
AMANTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS contains Amantadine Hydrochloride B.P. 100 mg.
3 Strips of 10 Tablets per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular