500 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
FOSNACIN-500 (Fosfomycin Calcium) is an antibacterial isolated from Streptomyces fradiae and other Streptomyces spp. or produced synthetically. Chemically, Fosfomycin Calcium is calcium (2R,3S)-(3-methyloxiran-2-yl) phosphonate. The molecular formula is C3H5CaO4P.H2O and molecular weight is 194.1.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
-Structure.jpg)
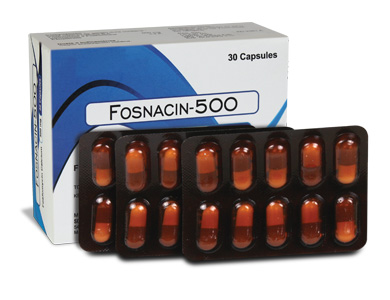
FOSNACIN-500 is a hard gelatin capsule containing a white or almost white powder.
COMPOSITION :
Each hard gelatin capsule contains :
Fosfomycin Calcium B.P.
equivalent to Fosfomycin 500 mg
Excipients q.s.
Approved colours used in empty capsule shells.
ACTIONS :
Fosfomycin inactivates enolpyruvyl transferase, which irreversibly blocks the condensation of uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine with phosphoenolpyruvate, and inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis. Fosfomycin also decreases the adherence of bacteria to epithelial cells of the urinary tract.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Fosfomycin calcium is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak plasma concentrations about 4 hours after a 1 g dose of fosfomycin calcium are around 7 micrograms/ml, and bioavailability has been calculated at about 30 to 40 %. Fosfomycin does not appear to be bound to plasma proteins. It crosses the placenta and is widely distributed in body fluids including the CSF; small amounts have been found in breast milk and bile. The majority of a parenteral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine, by glomerular filtration, within 24 hours.
INDICATIONS :
FOSNACIN-500 is indicated only for the treatment of uncomplicated urinary tract infections (acute cystitis) in women due to susceptible strains of Escherichia coli and Enterococcus faecalis. FOSNACIN-500 is not indicated for the treatment of pyelonephritis or perinephric abscess. If persistence or reappearance of bacteriuria occurs after treatment with FOSNACIN-500, other therapeutic agents should be selected.
Administration :
For Oral Use.
Dosage :
In the treatment of acute uncomplicated infections of the urinary tract, the usual adult dose of fosfomycin calcium by mouth is the equivalent of 1 gm fosfomycin every 6 to 8 hours. Fosfomycin has also been used with beta lactam antibacterials.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
FOSNACIN-500 is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug.
WARNINGS :
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhoea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including FOSNACIN-500, and may range in severity from mild diarrhoea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of Clostridium difficile. Clostridium difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of Clostridium difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhoea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents. If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against Clostridium difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of Clostridium difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
PRECAUTIONS :
Do not use more than one single dose of FOSNACIN-500 to treat a single episode of acute cystitis. Repeated daily doses of fosfomycin calcium did not improve the clinical success or microbiological eradication rates compared to single dose therapy, but did increase the incidence of adverse events. rine specimens for culture and susceptibility testing should be obtained before and after completion of therapy.
Pregnancy : Teratogenic Effects Category B
Fosfomycin calcium crosses the placental barrier of rats; it does not produce teratogenic effects in pregnant rats at dosages as high as 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 9 and 1.4 times the human dose based on body weight and mg/m2, respectively). When administered to pregnant female rabbits at dosages as high as 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 9 and 2.7 times the human dose based on body weight and mg/m2, respectively), foetotoxicities were observed. However, these toxicities were seen at maternally toxic doses and were considered to be due to the sensitivity of the rabbit to changes in the intestinal microflora resulting from the antibiotic administration. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing mothers :
It is not known whether fosfomycin calcium is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from
FOSNACIN-500, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to not administer the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Paediatric Use :
Safety and efficacy have not been established in children upto 12 years of age.
Geriatric Use :
Clinical studies of Fosfomycin calcium did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Gastrointestinal disturbances including nausea and diarrhoea, transient increases in serum concentrations of aminotransferases, headache, visual disturbances, and skin rashes have been reported following the use of fosfomycin. Eosinophilia and, rarely, angioedema, aplastic anaemia, exacerbation of asthma, cholestatic jaundice, hepatic necrosis, and toxic megacolon, have also occurred.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS :
Patients should be informed :
• That FOSNACIN-500 (Fosfomycin Calcium Capsules ) can be taken with or without food.
• That their symptoms should improve in two to three days after taking FOSNACIN-500; if not improved, the patient should contact her health care provider.
• Diarrhoea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular