50 mg/ml
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
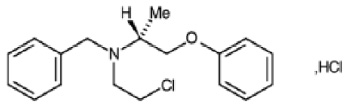
PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION (Phenoxybenzamine Hydrochloride) is a non-selective alpha-adrenoceptor antagonist. Chemically, Phenoxybenzamine Hydrochloride is (RS)-benzyl (2-chloroethyl) 1-methyl-2-phenoxyethylamine hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C18H22ClNO.HCl and molecular weight is 340.3.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION is a sterile, clear, colourless to mid – straw solution filled in amber ampoule of suitable size.
COMPOSITION :
Each ml contains :
Phenoxybenzamine Hydrochloride B.P. 50 mg
Ethanol B.P. 70 % v/v
Propylene Glycol B.P. q.s.
Contains no preservatives.
ACTIONS :
Phenoxybenzamine Hydrochloride is non competitive long acting α – adrenergic receptor antagonist.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Phenoxybenzamine is incompletely and variably absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral dosage the onset of action is gradual over several hours and persists for 3 or 4 days following a single dose. The maximum effect is attained in about 1 hour after an intravenous dose. The plasma half-life after intravenous dosage is about 24 hours. Phenoxybenzamine is metabolised in the liver and excreted in the urine and bile, but small amounts remain in the body for several days. The duration of action is thought to depend on the rate of synthesis of new alpha receptors following irreversible covalent bonding to existing alpha receptors by a reactive intermediate of phenoxybenzamine.
INDICATIONS :
In the management of phaeochromocytoma and as an adjunct to the treatment of severe shock not responding to conventional therapy in the presence of an adequate circulatory blood volume.
Administration :
For Intravenous Infusion after dilution.
PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION must be diluted before use.
The dose selected should be added aseptically to 200-500 ml 0.9 % sodium chloride immediately before use. The intravenous route only must be used, preferably through a large vein. Not more than one dose should be given in 24 hours, infused over at least two hours. It is suggested that one-third of the dose is given over the first hour, and the remaining two-thirds over the second hour if no precipitous fall in blood pressure has occurred.
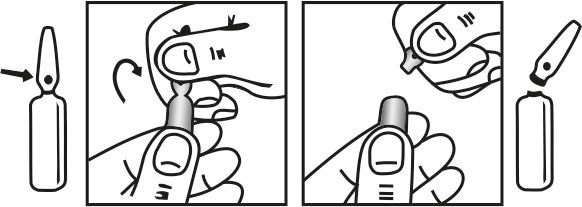
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF AMPOULE :
The ampoule used in this product is equipped with O.P.C (One Point Cut) opening system. No ampoule file is needed to open the ampoule. The neck of the ampoule is prescored at the point of constriction. A coloured dot on the ampoule head helps to orientate the ampoule. Take the ampoule and face the coloured dot. Let the solution at the head of the ampoule to flow down by shaking or a gentle stroke. The ampoule opens easily by placing the thumb on the coloured dot and gently pressing downwards as shown.
Dosage :
Adults and Elderly :
Must be diluted in physiological saline before use. Not more than one dose should be given in 24 hours, and not more than two doses in 48 hours.
Phaeochromocytoma : Dose titrated on daily basis : Guide daily dose 1 mg/kg body weight in 200 ml physiological saline over 2 hours.
Shock : 1 mg/kg body weight in 200-500 ml physiological saline over not less than 2 hours.Patient should be recumbent and blood pressure must be determined every few minutes during infusion.
Children : Dosage in children has not been established.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
Conditions where a fall in blood pressure may be undesirable; hypersensitivity to the drug or any of its components. Do not use in patients who have had a cerebrovascular accident; or in the recovery period (usually 3 - 4 weeks) after acute myocardial infarction. Do not use in the presence of hypovolaemia in patients with severe shock.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
The patient should be recumbent. Blood pressure must be determined every few minutes during the administration. Facilities for rapid infusion of intravenous fluid should be available. The phenoxybenzamine infusion should be slowed or stopped if there is a precipitous fall in blood pressure. This usually indicates an inadequate circulating blood volume, but occasionally may occur in the presence of an adequate blood volume in the hypertensives or in patients with carbon dioxide retention and in those cases is relatively unresponsive to the administration of intravenous fluids. Nevertheless, if severe hypotension does occur, treatment can be attempted with plasma expanders and the “head down” position. Noradrenaline may be of little value when α-adrenergic receptors are blocked. Adrenaline
should not be used since stimulation of β-adrenergic receptors will further decrease blood pressure. If blood pressure has been stabilised by the administration of appropriate fluids the PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION may be restarted under close supervision.
The blockage produced is often still exerting an effect 24 hours after administration and even in patients with a favourable response close attention to their cardiovascular status should be administration of phenoxybenzamine within 24 hours and the drug should not be given more than twice during a 48 hour period. Use with great caution in patients in whom a fall in blood pressure and/or tachycardia may be undesirable, such as the elderly or those with severe ischaemic heart disease, congestive heart failure, extensive arteriosclerosis, cerebrovascular disease or renal damage the adrenergic blocking effect may aggravate symptoms or respiratory infections. Alpha-sympathomimetics may be ineffective if used concomitantly with phenoxybenzamine. Care should be taken if phenoxybenzamine is used concomitantly with myocardial depressants e.g. beta-blockers and anti-arrhythmics. Extravasation should be avoided, as the diluted solution is an irritant to muscle tissue. Contamination of the hands should be avoided as reactions may occur in sensitive skins. Phenoxybenzamine is carcinogenic in the rat and has shown mutagenic activity in the bacterial ames test and mouse lymphoma assay. It should only be used after very careful consideration of the risks, in patients in which alternative treatment is inappropriate.
Pregnancy : Category C
Adequate reproductive studies in animals have not been performed with phenoxybenzamine hydrochloride. It is also not known whether PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION can cause foetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing mothers :
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from phenoxybenzamine hydrochloride, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Paediatric Use :
Safety and effectiveness in paediatric patients have not been established.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Phenoxybenzamine hydrochloride may interact with compounds that stimulate both alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptors (i.e., epinephrine) to produce an exaggerated hypotensive response and tachycardia PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION blocks hyperthermia production by levarterenol, and blocks hypothermia production by reserpine.
SIDE EFFECTS :
PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION given intravenously has a sedative effect and patients may become more drowsy or less responsive during infusion. This may occur in spite of an excellent cardiovascular response and should not be confused with the decreased responsiveness associated with the worsening shock syndrome. Other side effects include orthostatic hypotension with dizziness and compensatory tachycardia, miosis, dry mouth, nasal congestion, decreased sweating and gastrointestinal upset.
Convulsions have been reported after rapid infusion. Some fall in blood pressure is a normal response but an idiosyncratic profound hypotensive effect can occur usually with five minutes of starting the infusion. The effects of one dose of PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION on sympathetic motor response may last 48 hours or more.
OVERDOSAGE AND TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
There may be a precipitous fall in blood pressure even at the recommended dosage. Facilities for rapid infusion of intravenous fluid should therefore be available and in the event of such a severe hypotensive episode the PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION should be slowed or stopped. Treatment can be attempted with plasma expanders and the “head down” position. Noradrenaline may be of little value when alpha adrenergic receptors are blocked and adrenaline is contra-indicated.
PHARMACEUTICAL PRECAUTIONS :
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
PHENOXYBENZAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION is supplied as Phenoxybenzamine Hydrochloride B.P.
50 mg in 1 ml solution.
Such 1 ampoule of 1 ml is packed in a box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular