1 mg/ml
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION (Tetracosactide) is a corticotropic peptide. Chemically, Tetracosactide is sequence of amino acids which is same as that of the first 24 residues of human corticotrophin. The molecular formula is C136H210N40O31S and molecular weight is 2933.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
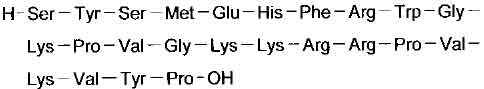
TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION is a sterile, milky-white, flocculent suspension filled in amber ampoule of suitable size which settles slowly on standing and is readily resuspended on shaking.
COMPOSITION :
Each ml contains :
Tetracosactide B.P. 1 mg
(as acetate)
Zinc Chloride B.P. (anhydrous)
equivalent to Zinc 2.5 mg
Water for Injections B.P. q.s.
ACTIONS :
Tetracosactide acetate consists of the first 24 amino acids occurring in the ACTH sequence and displays the same physiological properties as ACTH. In the adrenal cortex, it stimulates the biosynthesis of glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and, to a lesser extent androgens. The site of action of ACTH is the plasma membrane of the adrenocortical cells, where it binds to a specific receptor. The hormone-receptor complex activates adenylate cyclase, stimulating the production of cyclic AMP (adenosine monophosphate) and so promoting the synthesis of pregnenolone from cholesterol. From pregnenolone the various corticosteroids are produced via different enzymatic pathways.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Absorption :
Adsorption of tetracosactide to zinc oxide ensures sustained release of the active substance from the intramuscular injection site. Free tetracosactide is rapidly absorbed from the I.M. injection site. After an intramuscular injection of 1 mg TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC
INJECTION, the radioimmunologically determined plasma concentrations of tetracosactide range between 200 and 300 pg/ml and are maintained for 12 hours.
Distribution :
Tetracosactide is rapidly distributed and concentrated in the adrenals and kidneys, which lead to rapid decrease in its plasma levels. There is no evidence of binding of ACTH to any particular plasma protein. Tetracosactide has an apparent distribution volume of about 0.4 L/kg. Tetracosactide apparently does not cross the placenta and it is knknown whether tetracosactide passes into the breast milk.
Biotransformation / Metabolism :
In serum, tetracosactide is rapidly degraded by enzymatic hydrolysis, first to inactive oligopeptides, then to free amino acids. Its rapid elimination from plasma is probably attributable not so much to this relatively slow process as to the fact that the active substance is rapidly concentrated in the adrenals and kidneys.
Elimination :
Following an intravenous dose of 131I-labelled beta-24-corticotrophin, 95 to 100 % of the radioactivity is excreted in the urine within 24 hours.
Clinical studies :
No recent clinical trial was conducted with TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION.
Non-clinical safety data :
No studies have been performed to evaluate the mutagenic or carcinogenic potential of tetracosactide. No standard animal studies on fertility and reproduction toxicity have been performed with tetracosactide.
INDICATIONS :
Diagnostic use :
In cases of suspected adrenocortical insufficiency, where the 30-minute diagnostic test with TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION has yielded inconclusive results or where it is desired to determine the functional reserve of the adrenal cortex, a 5-hour test with TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION may be performed.
Therapeutic use :
Neurological diseases :
Acute exacerbations in patients suffering from multiple sclerosis.West syndrome (Infantile myoclonic encephalopathy with hypsarrhythmia).
Rheumatic diseases :
Short-term therapy in conditions for which glucocorticoids are normally indicated; in patients showing poor gastrointestinal tolerance of oral glucocorticoids; where glucocorticoids in normal doses have not elicited an adequate response.
Skin diseases :
Long-term treatment of skin disorders responsive to glucocorticoids - e.g. pemphigus, severe chronic eczema, erythrodermal or pustular forms of psoriasis.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract :
Ulcerative colitis; regional enteritis.
Oncology :
As adjuvant therapy to improve the tolerability of chemotherapy.
Administration :
TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION is for I.M. use only.
NOT FOR INTRAVENOUS USE. THE AMPOULE SHOULD BE GENTLY SHAKEN BEFORE A DOSE IS WITHDRAWN.
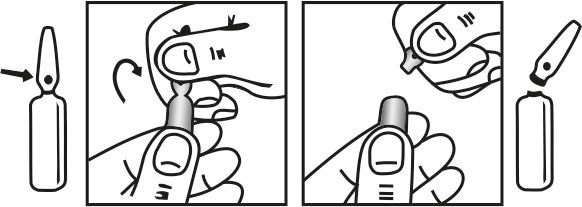
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE OF AMPOULE :
The ampoule used in this product is equipped with O.P.C. (One Point Cut) opening system. No ampoule file is needed to open the ampoule. The neck of the ampoule is prescored at the point of constriction. A coloured dot on the ampoule head helps to orientate the ampoule. Take the ampoule and face the coloured dot. Let the solution at the head of the ampoule to flow down by shaking or a gentle stroke. The ampoule opens easily by placing the thumb on the coloured dot and gently pressing downwards as shown.
Dosage :
Diagnostic use for the investigation of adrenocortical insufficiency :
5-hour TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION test : Plasma cortisol is measured immediately before and 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 hours after an intramuscular injection of 1 mg TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION. If plasma cortisol rises more slowly than indicated above, this may be the result of : Addison’s disease; secondary adrenocortical insufficiency due to a disorder of hypothalamo-pituitary function, or overdose of corticosteroids. For further differentiation between primary and secondary adrenocortical hypofunction, a 3-day test can be performed using TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION. All the plasma samples should be stored in a refrigerator until plasma cortisol level estimation.
Therapeutic use :
Treatment is initiated with daily doses of TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION and continued with intermittent doses after about 3 days.
Adults :
The initial dose is 1 mg daily administered intramuscularly; in acute cases and in oncological indications, treatment can be started with 1 mg every 12 hours. Once the acute manifestations have subsided, the usual dosage is 1 mg every 2 to 3 days; in patients who respond well, the dosage may be reduced to as little as 0.5 mg every 2 to 3 days or 1 mg weekly.
Special populations :
Renal impairment :
No studies have been performed in patients with renal impairment.
Hepatic impairment :
No studies have been performed in patients with hepatic impairment.
Paediatric patients :
1 month to less than 2 years : Initially 0.25 mg daily administered intramuscularly; the maintenance dose is 0.25 mg every 2 to 8 days. 2 to less than 5 years : Initially 0.25 to 0.5 mg daily administered intramuscularly; the maintenance dose is 0.25 to 0.5 mg every 2 to 8 days.
5 to less than 12 years : Initially 0.25 to 1 mg daily administered intramuscularly; the maintenance dose is 0.25 to 1 mg every 2 to 8 days.
Geriatric patients :
There is no such information available which would necessitate dosage modification in elderly (65 years of age and above).
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
History of hypersensitivity to Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION.
TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION is contra-indicated in patients with allergic disorders (e.g. asthma), acute psychosis, infectious diseases, peptic ulcer, refractory heart failure, Cushing’s syndrome, and primary adrenocortical insufficiency, adrenogenital syndrome.
TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION should not be used during pregnancy or lactation unless there are compelling reasons to do so.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION should not be administered intravenously. Before using TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION, the doctor should make every effort to find out whether the patient is suffering from, or has a history of, allergic disorders. In particular, he should enquire whether the patient has previously experienced adverse reactions to ACTH, TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION or other drugs. TRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION should only be administered under the supervision of appropriate senior hospital medical staff (e.g. consultants).
If local or systemic hypersensitivity reactions occur after the injection (for example, marked redness and pain at the injection site, urticaria, pruritus, flushing, faintness or dyspnoea), TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION or other ACTH preparations should be avoided in the future. Hypersensitivity reactions tend to occur within 30 minutes of an injection. The patient should therefore be kept under observation during this time. Preparation should be made in advance to combat any anaphylactic reaction that may occur after an injection of TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION. In the event of a serious anaphylactic reaction
occurring, the following measures must be taken immediately :
administer adrenaline (0.4 to 1 ml of a 0.1 % solution intramuscularly or 0.1 to 0.2 ml of a 0.1 % solution in 10 ml physiological saline slowly intravenously) as well as a large intravenous dose of a corticosteroid (for example 100 mg to 500 mg hydrocortisone, three or four times in 24 hours), repeating the dose if necessary.
Post administration total plasma cortisol levels during the TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION test might be misleading in some special clinical situations due to altered cortisol binding globulin levels. These situations include patients on oral contraceptives, post operative patients, critical illness, severe liver disease, nephrotic syndrome. Hence, in these circumstances, alternative parameters (e.g., salivary cortisol, free cortisol index, plasma free cortisol) can be used to assess the integrity of HPA axis. Salt and water retention in response to TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION can often be avoided or eliminated by prescribing a low-salt diet. During prolonged treatment, potassium substitution may occasionally be required. The effect of tetracosactide therapy may be increased in patients with hypothyroidism or cirrhosis of the liver.
Prolonged tetracosactide therapy may be associated with development of posterior subcapsular cataracts and glaucoma. Psychological disturbances may occur under treatment with tetracosactide (e.g. euphoria, insomnia, mood swings, personality changes and severe depression, or even frank psychotic manifestations). Existing emotional instability or psychotic tendencies may be aggravated. TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION should be used cautiously in patients with ocular herpes simplex owing to possible corneal perforation.
TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION may activate latent amoebiasis. It is therefore recommended that latent or active amoebiasis be ruled out before initiating therapy. If TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION is indicated in patients with latent tuberculosis or tuberculin reactivity, close observation is necessary because the disease may be reactivated. During prolonged therapy, such patients should receive chemoprophylaxis.Live virus immunisation procedures must not be undertaken during treatment with TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION because of the decrease in antibody response.
Provided the dosage is carefully individualised, TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION is unlikely to inhibit growth in children. Nevertheless, growth should be monitored in children undergoing long-term treatment. Echocardiography should be performed regularly in infants and small children since reversible cardiac hypertrophy may occurring long-term treatment with high doses. If TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION is used in any of the following conditions, the risks of treatment should be weighed against the possible benefits : ulcerative colitis, diverticulitis, recent intestinal anastomosis, renal insufficiency, hypertension, predisposition to thromboembolism, osteoporosis, myasthenia gravis. In patients who suffer an injury or undergo surgery during or within one year after treatment, the associated stress should be managed by an increase in or resumption of treatment with TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION. Additional use of rapidly acting corticosteroids may be required. Use the lowest effective dose to control the condition under treatment. If the dose has to be reduced, this should be done gradually. Relative insufficiency of the pituitary-adrenal axis is induced by prolonged administration, and may persist for several months after stopping treatment, so appropriate adrenocortical therapy should be considered.
Pregnancy : Category C
There is limited amount of data in the use of tetracosactide in pregnant women. Animal studies are insufficient with respect to reproductive toxicity. Usage in pregnancy is contraindicated. Therefore the tetracosactide should not be utilised during pregnancy and lactation unless there are compelling reasons for doing so.
Nursing mothers :
It is not known whether tetracosactide enters breast milk or not. Usage in lactation is contraindicated.
Paediatric use :
Appropriate studies on the relationship of age to the effects of tetracosactide have not been performed in the paediatric population. However, no paediatrics-specific problems have been documented to date.
EFFECTS ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
Patients should be warned of the potential hazards of driving or operating machinery if they experience side effects such as dizziness.
INTERACTIONS :
Observed interactions resulting in concomitant use not being recommended :
Severe jaundice has been observed for concurrent use of tetracosactide and valproate in paediatric population. Their concurrent use should be avoided.
Observed interactions to be considered :
Concurrent use of tetracosactide and other anticonvulsants (e.g. phenytoin, clonazepam, nitrazepam, phenobarbital, primidone) may increase the risk of liver damage, thus, TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION should be used with caution at minimum possible doses and for minimum duration for concurrent treatment. Endogenous and synthetic estrogens can cause an increase in total cortisol levels and therefore, it is considered appropriate to use alternative methods (e.g., salivary cortisol, free cortisol index, plasma free cortisol) for interpretation of the results of the HPA axis examination.
Anticipated interactions to be considered :
Since tetracosactide increases the adrenocortical production of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, drug interactions of the type seen with these corticosteroids may occur. Patients already receiving medication for diabetes mellitus or for moderate to severe hypertension must have their dosage adjusted if treatment with tetracosactide is started.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Undesirable effects related to tetracosactide :
Hypersensitivity reactions :
Tetracosactide can provoke hypersensitivity reactions, which tend to be more severe (anaphylactic shock) in patients susceptible to allergies (especially asthma). Hypersensitivity reactions may include skin reactions at the injection site, dizziness, nausea, vomiting,
urticaria, pruritus, flushing, malaise, dyspnoea, and angioneurotic oedema or Quincke’s oedema.
Adrenal haemorrhage :
Isolated cases have been reported with TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION.
OVERDOSAGE :
Signs and Symptoms :
If signs of water retention (increase in body weight) or excessive adrenocortical activity (Cushing’s syndrome) appear, TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION should either be withdrawn for a while or given in lower doses, either by halving the dose or by prolonging the interval between injections, e.g. to 5 to 7 days.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
There is no known antidote. Symptomatic treatment is indicated.
STORAGE :
Store in a refrigerator between 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F), protected from light.
Do not freeze.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
TETRACOSACTIDE ZINC INJECTION is supplied as 1 mg of Tetracosactide (as acetate) B.P. in 1 ml aqueous suspension.
Single Ampoule per Box.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular