10 mg, 25 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
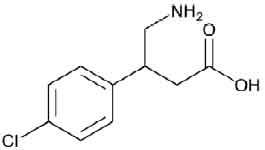
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP (Baclofen) is a muscle relaxant and antispastic. Chemically, Baclofen is β-(Aminomethyl)-p-chlorohydrocinnamic acid. The molecular formula is C10H12ClNO2 and molecular weight is 213.66.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP 5 mg are white to off white, circular, biconvex tablets having score line on one side and “SGP” embossed on the other side of each tablet.
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP 10 mg are white to off white, circular, biconvex tablets having score line on one side and “SGP” embossed on the other side of each tablet.
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP 25 mg are white to off white, circular, biconvex tablets having score line on one side and “SGP” embossed on the other side of each tablet.
COMPOSITION :
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Baclofen USP 5 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Baclofen USP 10 mg
Excipients q.s.
Each uncoated tablet contains :
Baclofen USP 25 mg
Excipients q.s.
ACTIONS :
Baclofen, an analogue of gamma-aminobutyric acid, is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant. It interferes with the release of excitatory neurotransmitters and inhibits monosynaptic and polysynaptic transmission at the spinal cord level. It may also act at supraspinal sites producing CNS depression. Baclofen is one of the drugs commonly used for the symptomatic relief of severe chronic spasticity associated with a variety of conditions.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
Baclofen is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract following an oral dose. Peak plasma concentrations occur about 0.5 to 3 hours after ingestion, but the rate and extent of absorption vary between patients, and may vary inversely with the dose. After oral doses some baclofen crosses the blood-brain barrier, with concentrations in CSF about 12 % of those in the plasma. Approximately 30 % of baclofen is bound to plasma proteins. About 70 to 80 % of a dose is excreted in the urine mainly as unchanged drug; about 15 % is metabolised in the liver. The elimination half-life of baclofen is about 3 to 4 hours in plasma and about 1 to 5 hours in the CSF. Baclofen crosses the placenta and is distributed into breast milk.
Absorption :
A crossover study in 5 healthy subjects given baclofen 20 mg by mouth after an overnight fast or a standardised breakfast showed that baclofen was rapidly absorbed in both cases, and the rate and extent of absorption were not significantly altered by the presence of food. There is no need to modify the current practice of giving baclofen with food to minimise gastrointestinal side-effects.
INDICATIONS :
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP is indicated to relieve the signs and symptoms of spasticity caused by multiple sclerosis, spinal cord diseases, or spinal cord injury. It is especially useful in relieving flexor spasms and concomitant pain, clonus, and muscular rigidity.
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP may also improve bowel and bladder function in some patients with spinal lesions; however, it may not improve spastic stiff gait or manual dexterity. BACLOFEN TABLETS USP is used to reduce the number and severity of attacks of trigeminal neuralgia in patients who are not able to tolerate, or who have become refractory to the effects of, carbamazepine. In some patients, baclofen may provide additional benefit when used concurrently with carbamazepine.
Administration :
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP is for oral administration.
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP should be taken during meals with a little liquid.
Dosage :
Treatment should always be initiated with small, gradually increasing doses of BACLOFEN TABLETS USP. The optimum daily dosage should be individually adapted to the patient’s requirements in such a way that clonus, flexor and extensor spasms, and spasticity are reduced, but that side effects are as far as possible avoided. In order to prevent excessive weakness and falling, BACLOFEN TABLETS USP should be used with caution when spasticity is needed to sustain upright posture and balance in locomotion or whenever spasticity is used to maintain function. It may be important to maintain some degree of muscle tone and allow occasional spasms to help support circulatory function. The daily dosage should be given in divided doses, preferably 3 in adults and 4 in children.
Adults :
Treatment should as a rule be started with a dosage of 5 mg, 3 times daily, which, for the purpose of cautious dose titration, should subsequently be increased at 3-day intervals by 5 mg, 3 times daily until the requisite daily dosage has been attained. In certain patients reacting sensitively to medicines, it may be advisable to begin with a lower daily dosage (5 mg or 10 mg) and to raise this dosage more gradually. The optimum dosage generally ranges from 30 mg to 80 mg daily. Daily doses of 100 to 120 mg may be given to carefully supervised patients in hospital.
Children :
Treatment should usually be started with a very low dose, e.g. 0.3 mg/kg a day, in divided doses. The dosage should be raised cautiously, at about 1 to 2 week intervals, until it becomes sufficient for the child’s individual requirements. The usual daily dosage for maintenance therapy ranges between 0.75 and 2 mg/kg body weight. In children over 10 years of age, however, a maximum daily dosage of 2.5 mg/kg body weight may be given. If no benefit is apparent within 6 to 8 weeks of achieving the maximum dosage, a decision whether to continue with BACLOFEN TABLETS USP should be taken.
Impaired Renal Function :
In patients with impaired renal function baclofen should be given with caution and in lower doses. In patients undergoing chronic haemodialysis, baclofen concentrations in plasma are elevated and therefore a particularly low dosage of BACLOFEN TABLETS USP should be selected, i.e. approx. 5 mg daily.
Elderly :
Since unwanted effects are more likely to occur in elderly patients or in patients with spastic states of cerebral origin, it is recommended that a very cautious dosage schedule be adopted in such cases and that the patient be kept under appropriate surveillance.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
BACLOFEN TABLETS USP are contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to baclofen. BACLOFEN TABLETS USP contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS :
Psychotic disorders, confusional states, schizophrenia, depressive or manic disorders or Parkinson’s disease may be worsened by treatment with baclofen. Therefore, patients with these conditions should be kept under close observation and treatment should be administered cautiously. Epileptic manifestations may be exacerbated with baclofen treatment, but may be used if appropriate supervision and anticonvulsive therapy are maintained. Baclofen should be used with extreme care in patients already receiving antihypertensive therapy. Caution should be exercised with baclofen therapy in patients suffering from renal, hepatic or respiratory impairment or who have had a cerebrovascular accident.
Patients with neurogenic disturbances affecting emptying of the bladder may show improvement in their condition whilst taking baclofen. However, patients with pre-existing sphincter hypertonia may suffer with acute urine retention during treatment with baclofen; as a result it should be used cautiously in these patients. Appropriate laboratory tests should be carried out on patients with hepatic dysfunction or diabetes mellitus to make sure that no drug-induced changes to the underlying diseases have resulted with concomitant baclofen therapy as, rarely, elevated SGOT, alkaline phosphatase and glucose levels in serum have been recorded. Baclofen therapy should always be gradually discontinued, unless serious adverse effects have occurred, by reducing the dose over a period of 1-2 weeks. Anxiety, confusion, hallucinations, psychosis, mania, paranoia, convulsions, tachycardia, and, as a rebound phenomenon, temporary aggravation of spasticity, have all been reported on abrupt withdrawal.
Pregnancy :
Not recommended in pregnancy as foetal malformations have been reported as having occurred in rats but not mice or rabbits. Where treatment is necessary, the benefits for the mother should be carefully considered against the possible risks to the child, particularly in the first trimester when baclofen should only be used if essential.
Nursing mothers :
Baclofen is not recommended whilst breast-feeding as it is known to be present in the milk.
EFFECTS ON ABILITY TO DRIVE AND USE MACHINES :
Patients taking baclofen should not take charge of vehicles, other means of transport, or machinery where loss of attention may lead to accidents.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
There have been reports of hallucinations, agitation and mental confusion with the use of baclofen with levodopa and carbidopa in Parkinson’s disease. Use of tricyclic antidepressants and baclofen may result in the potentiation of the effect of baclofen, resulting in pronounced muscular hypotonia. Baclofen excretion may be reduced by drugs which produce renal insufficiency, eg ibuprofen, resulting in toxic effects. Concomitant use of drugs acting on the CNS or alcohol with baclofen may lead to increased sedation. The risk of respiratory depression is also increased. Careful monitoring of respiratory and cardiovascular functions is essential especially in patients with cardiopulmonary disease and respiratory muscle weakness.
Fentanyl induced analgesia may be extended by pre-treatment with baclofen. Hyperkinetic symptoms in patients receiving lithium may be exacerbated by baclofen. Antihypertensive therapy may require adjustment as an increased fall in blood pressure may result with concomitant treatment with baclofen.
SIDE EFFECTS :
Side effects associated with baclofen are often transient and dose-related. They may be minimised by increasing doses gradually or controlled by a reduction in dosage. The most common side-effects include drowsiness, nausea, dizziness, lassitude, lightheadedness, confusion, fatigue, muscular pain and weakness, and hypotension. Other side-effects include euphoria, hallucinations, depression, headache, tinnitus, convulsions, paraesthesias, slurred speech, dry mouth, taste alterations, vomiting, diarrhoea or constipation, ataxia, nystagmus, tremors, insomnia, visual disturbances, skin rashes, pruritus, increased sweating, urinary disturbances, respiratory or cardiovascular depression, blood sugar changes, alterations in liver function values, and a paradoxical increase in spasticity. Problems with erection and ejaculation have also been reported with intrathecal baclofen ; these are usually reversible on withdrawal of therapy. Abrupt withdrawal of baclofen may result in a withdrawal syndrome.
OVERDOSAGE AND TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
Symptoms :
Primarily, these are signs of central nervous depression :
including drowsiness, consciousness impairment, respiratory depression, coma. Also likely are confusion, agitation, hallucinations, eye accommodation disorders, absent pupillary reflex, generalised muscular hypotonia, myoclonia, hyporeflexia or areflexia, convulsions, peripheral vasodilatation, hypotension, bradycardia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, hyper salivation and elevated LDH, SGOT and AP values. Deterioration in the condition may occur if various substances/drugs acting on the CNS, eg alcohol, tricyclic antidepressants or diazepam, have been taken at the same time.
Treatment :
No specific antidote is known. Removal of the drug from the gastro-intestinal tract should be attempted by inducing vomiting or gastric lavage. Comatose patients need to be intubated prior to gastric lavage. Activated charcoal or, if necessary, a saline aperient may be given. In respiratory depression, artificial respiration and measures to support cardiovascular functions should be applied. Large quantities of fluid should be given, possibly with a diuretic, since baclofen is excreted mainly through the kidneys. If convulsions occur, intravenous diazepam should be administered.
STORAGE :
Store below 30°C (86°F), protected from moisture and light.
Do not refrigerate.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from date of manufacture.
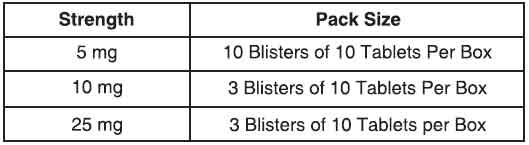
PRESENTATION :
Baclofen tablets usp is supplied as per below table.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular