2 mg, 5 mg
For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only.
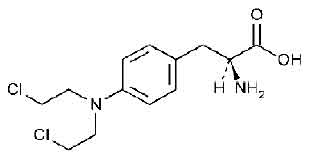
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP (Melphalan) is also known as L-phenylalanine mustard, phenylalanine mustard, L-PAM, or L-sarcolysin, is a phenylalanine derivative of nitrogen mustard. Melphalan is a bifunctional alkylating agent which is active against selective human neoplastic diseases. Chemically, melphalan is L-Phenylalanine, 4-bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]-.The molecular formula is C13H18Cl2N2O2 and molecular weight is 305.20.
STRUCTURAL FORMULA :
Its structural formula is :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP are white, film coated, round biconvex tablets.
COMPOSITION :
Each film-coated tablet contains :
Melphalan USP 2 mg
Excipients q.s.
Colour : Titanium Dioxide B.P.
ACTIONS :
Melphalan is an alkylating agent of the nitrogen mustard type. Melphalan is a bifunctional alkylating agent and is cell cycle-phase nonspecific. Activity occurs as a result of formation of an unstable ethylenimmonium ion, which alkylates or binds with many intracellular molecular structures including nucleic acids. Its cytotoxic action is primarily due to cross-linking of strands of DNA and RNA, as well as inhibition of protein synthesis.
PHARMACOKINETICS :
The absorption of melphalan was found to be highly variable in 13 patients given 0.6 mg/kg bodyweight orally, with respect to both the time to first appearance of the medicine in plasma (range 0 to 336 minutes) and peak plasma concentration (range 70 to 630 ng/ml). In 5 of the patients who were given an equivalent intravenous dose, the mean absolute bioavailability of melphalan was found to be 56 ± 27 %. The plasma mean terminal elimination half-life was 90 ± 57 minutes with 11 % of the medicine being recovered in the urine over 24 hours.
In a study of 18 patients administered melphalan 0.2 to 0.25 mg/kg bodyweight orally, a maximum plasma concentration (range 87 to 350 ng/ml) was reached within 0.5 to 2.0 hours. The mean elimination half-life was 1.12 ± 0.15 hours. The administration of melphalan immediately after food delayed the time to achieving peak plasma concentrations and reduced the area under the plasma concentration-time curves by between 39 and 45 %.
INDICATIONS :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP are indicated in the treatment of multiple myeloma and advanced ovarian adenocarcinoma. MELPHALAN TABLETS USP either alone or in combination with other drugs has a significant therapeutic effect in a proportion of patients suffering from advanced breast carcinoma. MELPHALAN TABLETS USP is effective in the treatment of a proportion of patients suffering from polycythaemia rubra vera.
Administration :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP is for oral administration. Since MELPHALAN TABLETS USP is myelosuppressive, frequent blood counts are essential during therapy and the dosage should be delayed or adjusted if necessary.
Oral administration in Adults :
The absorption of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP after oral administration is variable. Dosage may need to be cautiously increased until myelosuppresion is seen, in order to ensure that potentially therapeutic levels have been reached.
Multiple Myeloma :
Numerous regimens have been used and the scientific literature should be consulted for details. The administration of melphalan and prednisone is more effective than melphalan alone. The combination is usually given on an intermittent basis, although the superiority of this technique over continuous therapy is not established. A typical oral dosage scheduleis 0.15 mg/kg bodyweight/day in divided doses for 4 days repeated at intervals of six weeks. Prolonging treatment beyond one year in responders does not appear to improve results.
Ovarian adenocarcinoma :
A typical regimen is 0.2 mg/kg bodyweight/day orally for 5 days. This is repeated every 4 - 8 weeks, or as soon as the bone marrow has recovered. MELPHALAN TABLETS USP has also been used intravenously in the treatment of ovarian carcinoma.
Advanced carcinoma of the breast :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP has been given orally at a dose of 0.15 mg/kg bodyweight or 6 mg/m2 body surface area/day for 5 days and repeated every 6 weeks. The dose was decreased if bone marrow toxicity was observed.
Polycythaemia vera :
For remission induction the usual dose is 6 -10 mg daily for 5 - 7 days, after which 2 - 4 mg daily is given until satisfactory disease control is achieved. Therapy is maintained with a dose of 2 - 6 mg per week. During maintenance therapy, careful haematological control is essential with dosage adjustment according to the results of frequent blood counts.
Children :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP is very rarely indicated in children and dosage guidelines cannot be stated.
Use in the elderly :
There is no specific information available on the use of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP in elderly patients.
Dosage in renal impairment :
In patients with moderate to severe renal impairment currently available pharmacokinetic data do not justify an absolute recommendation on dosage reduction when administering the oral preparation to these patients, but it may be prudent to use a reduced dose initially.
CONTRAINDICATIONS :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP should not be given to patients who have suffered a previous hypersensitivity reaction to melphalan. MELPHALAN TABLETS USP contains lactose which is contra-indicated in patients with galactosaemia, the glucose-galactose malabsorption syndrome, or lactase deficiency.
WARNINGS :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP should be administered in carefully adjusted dosage by or under the supervision of experienced physicians who are familiar with the drug’s actions and the possible complications of its use. As with other nitrogen mustard drugs, excessive dosage will produce marked bone marrow suppression. Bone marrow suppression is the most significant toxicity associated with MELPHALAN TABLETS USP in most patients. Therefore, the following tests should be performed at the start of therapy and prior to each subsequent course of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP : platelet count, haemoglobin, white blood cell count, and differential. Thrombocytopaenia and/or leukopaenia are indications to withhold further therapy until the blood counts have sufficiently recovered. Frequent blood counts are essential to determine optimal dosage and to avoid toxicity. Dose adjustment on the basis of blood counts at the nadir and day of treatment should be considered. Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred rarely. These reactions have occurred after multiple courses of treatment and have recurred in patients who experienced a hypersensitivity reaction to IV melphalan. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, oral or IV melphalan should not be readministered.
Carcinogenesis :
Secondary malignancies, including acute nonlymphocytic leukemia, myeloproliferative syndrome, and carcinoma have been reported in patients with cancer treated with alkylating agents (including melphalan). Some patients also received other chemotherapeutic agents or radiation therapy. Precise quantitation of the risk of acute leukaemia, myeloproliferative syndrome, or carcinoma is not possible. Published reports of leukemia in patients who have received melphalan (and other alkylating agents) suggest that the risk of leukemogenesis increases with chronicity of treatment and with cumulative dose. In one study, the 10-year cumulative risk of developing acute leukemia or myeloproliferative syndrome after melphalan therapy was 19.5 % for cumulative doses ranging from 730 mg to 9,652 mg. In this same study, as well as in an additional study, the 10-year cumulative risk of developing acute leukemia or myeloproliferative syndrome after melphalan therapy was less than 2 % for cumulative doses under 600 mg. This does not mean that there is a cumulative dose below which there is no risk of the induction of secondary malignancy. The potential benefits from melphalan therapy must be weighed on an individual basis against the possible risk of the induction of a second malignancy. Adequate and well-controlled carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted in animals. However, i.p. administration of melphalan in rats (5.4 to 10.8 mg/m2) and in mice (2.25 to 4.5 mg/m2) 3 times per week for 6 months followed by 12 month post-dose observations produced peritoneal sarcoma and lung tumors, respectively.
Mutagenesis :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP has been shown to cause chromatid or chromosome damage in humans. Intramuscular administration of melphalan at 6 and 60 mg/m2 produced structural aberrations of the chromatid and chromosomes in bone marrow cells of Wistar rats.
PRECAUTIONS :
General :
In all instances where the use of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP is considered for chemotherapy, the physician must evaluate the need and usefulness of the drug against the risk of adverse events. MELPHALAN TABLETS USP should be used with extreme caution in patients whose bone marrow reserve may have been compromised by prior irradiation or chemotherapy, or whose marrow function is recovering from previous cytotoxic therapy. If the leukocyte count falls below 3,000 cells/mcl, or the platelet count below 100,000 cells/mcl, MELPHALAN TABLETS USP should be discontinued until the peripheral blood cell counts have recovered. A recommendation as to whether or not dosage reduction should be made routinely in patients with renal insufficiency cannot be made because :
a. There is considerable inherent patient-to-patient variability in the systemic availability of melphalan in patients with normal renal function.
b. Only a small amount of the administered dose appears as parent drug in the urine of patients with normal renal function.
Patients with azotemia should be closely observed, however, in order to make dosage reductions, if required, at the earliest possible time. MELPHALAN TABLETS USP should be used cautiously in diabetic patients.
Pregnancy : Category D
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP may cause foetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Melphalan was embryolethal and teratogenic in rats following oral (6 to 18 mg/m2/day for 10 days) and intraperitoneal (18 mg/m2) administration Malformations resulting from melphalan included alterations of the brain (underdevelopment, deformation,meningocele, and encephalocele) and eye (anophthalmia and microphthalmos), reduction of the mandible and tail, as well as hepatocele (exomphaly). There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant.
Teratogenicity :
The teratogenic potential of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP has not been studied. In view of its mutagenic properties and structural similarity to known teratogenic compounds, it is possible that MELPHALAN TABLETS USP could cause congenital defects in the offspring of patients treated with the medicine.
Effects on fertility :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP causes suppression of ovarian function in premenopausal women resulting in amenorrhoea in a significant number of patients. There is evidence from some animal studies that MELPHALAN TABLETS USP can have an adverse effect on spermatogenesis. Therefore, it is possible that MELPHALAN TABLETS USP may cause temporary or permanent sterility in male patients.
Nursing mothers :
Mother receiving MELPHALAN TABLETS USP should not breast-feed.
Paediatric Use :
The safety and effectiveness of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP in Paediatric patients have not been established.
INTERACTIONS AND INCOMPATIBILITIES :
Vaccinations with live organism vaccines are not recommended in immunocompromised individuals. Nalidixic acid together with high-dose intravenous melphalan has caused deaths in children due to haemorrhagic enterocolitis. Impaired renal function has been described in bone marrow transplant patients who were conditioned with high-dose intravenous melphalan and who subsequently received cyclosporin to prevent graft-versus-host disease.
SIDE EFFECTS :
The most common side effect is bone marrow depression, leading to leukopaenia, thrombocytopaenia and anaemia. Gastrointestinal effects such as nausea and vomiting have been reported in up to 30 % of patients receiving conventional oral doses of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP. Hepatic disorders ranging from abnormal liver function tests to clinical manifestations such as hepatitis and jaundice occur rarely. Stomatitis occurs rarely following conventional doses of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP. Allergic reactions to MELPHALAN TABLETS USP such as urticaria, oedema, skin rashes and anaphylactic shock have been reported uncommonly following initial or subsequent dosing, particularly after intravenous administration. Cardiac arrest has also been reported rarely in association with such events. Maculopapular rashes and pruritus have occasionally been noted. There have also been case reports of fatal pulmonary fibrosis and haemolytic anaemia occurring after melphalan treatment. Alopecia has been commonly reported at conventional doses and occurs very commonly at high doses.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS :
Patients should be informed that the major toxicities of MELPHALAN TABLETS USP are related to bone marrow suppression, hypersensitivity reactions, gastrointestinal toxicity, and pulmonary toxicity. The major long-term toxicities are related to infertility and secondary malignancies. Patients should never be allowed to take the drug without close medical supervision and should be advised to consult their physician if they experience skin rash, vasculitis, bleeding, fever, persistent cough, nausea, vomiting, amenorrhoea, weight loss, or unusual lumps/masses. Women of childbearing potential should be advised to avoid becoming pregnant.
OVERDOSAGE :
Symptoms and signs :
Gastro-intestinal effects, including nausea, vomiting and diarrhoea are the most likely early signs of acute oral overdosage. The principal toxic effect is bone marrow suppression, leading to leukopaenia, thrombocytopaenia and anaemia.
TREATMENT OF OVERDOSAGE :
General supportive measures, together with appropriate blood and platelet transfusions, should be instituted if necessary, and consideration given to hospitalization, cover with anti-infective agents, and the use of haematological growth factors. There is no specific antidote. The blood picture should be closely monitored for at least 4 weeks following overdosage until there is evidence of recovery.
STORAGE :
Store in a refrigerator between 2°C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F).
Do not freeze.
SHELF LIFE :
24 months from the date of manufacture.
PRESENTATION :
MELPHALAN TABLETS USP contains Melphalan USP 2 mg.
25 tablets are packed in a bottle.
Disclaimer : For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Institution only. Also it is not intended to be used by healthcare professionals or patients for the purpose of prescribing or administering these products. Questions regarding the complete and current content of product labeling / specification / presentation should be directed to SGPharma.
 Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular